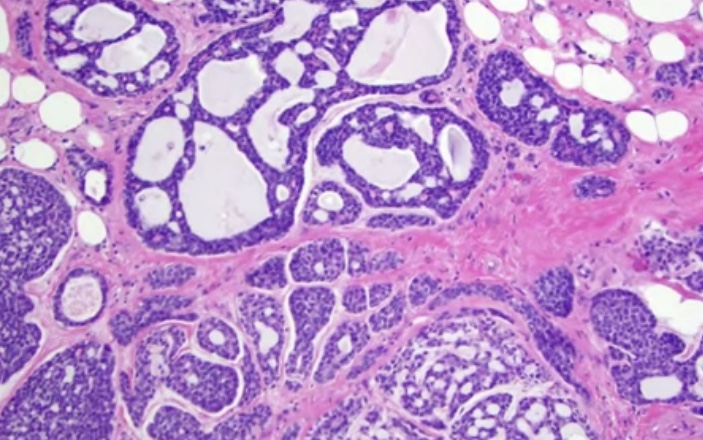
- Adenoid cystic carcinoma:
- 0.1% to 1% of all breast cancers
- Low aggressive malignant potential
- Myoepithelial differentiation
- Exhibit tubular, trabecular, cribriform, and / or solid patterns
- Cribriform is the classic pattern
- Characterized by MYB-NFIB t(6;9)(q22-23;p23-24)

- Tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TIL):
- Recommendations for assessing TILS in breast cancer:
- Evaluated for the stromal component (% of stromal TIL)
- Evaluated with the borders of the invasive tumor
- Exclude TILs outside of the tumor border, around DCIS and normal lobules
- Lymphocytes and plasma cells, exclude neutrophils
- Full sections are preferred over biopsies:
- Cores can be used in the pre therapeutic neoadjuvant setting
- Average TILs in the tumor area (do not focus on hotspots)
- The number of TILS correlate with complete pathologic response in the neoadjuvant setting
- No formal recommendations for a clinically relevant TILS threshold(s) can be given at this stage
- Recommendations for assessing TILS in breast cancer:
- PD-L1 and Breast Cancer:
- The PD-L1 on tumor cells, when combined with its PD-1 on immune cells:
- Causes an inhibition of immune response mediated by CD8+ T cells
- Breast tumor that have PD-L1 tend to have high number of TILs, and the majority are of the triple negative type
- The PD-L1 on tumor cells, when combined with its PD-1 on immune cells:
- Tumors arising in BRCA 1 carriers:
- BRCA 1 is involved in:
- DNA repair
- Cell cycle regulation
- Transcriptional regulation
- Chromatin remodeling
- Loss of BRCA 1 leads to:
- Deficiency in repair of DNA doble-strand breaks
- 75% of all tumors developing in BRCA 1 germ line mutation carriers are TNBC:
- High histologic grade
- High proliferation rate
- BRCA 1 is involved in:
- Residual cancer burden after neoadjuvant chemotherapy (NAC):
- Parameters required to calculate residual cancer burden (RCB):
- Submission of the entire area of the tumor bed
- Tumor dimensions (at least in two dimensions)
- Percentage invasive carcinoma in the tumor bed
- Percentage of the in situ carcinoma in the tumor bed
- The number of positive lymph nodes
- The largest diameter of nodal metastasis
- Parameters required to calculate residual cancer burden (RCB):
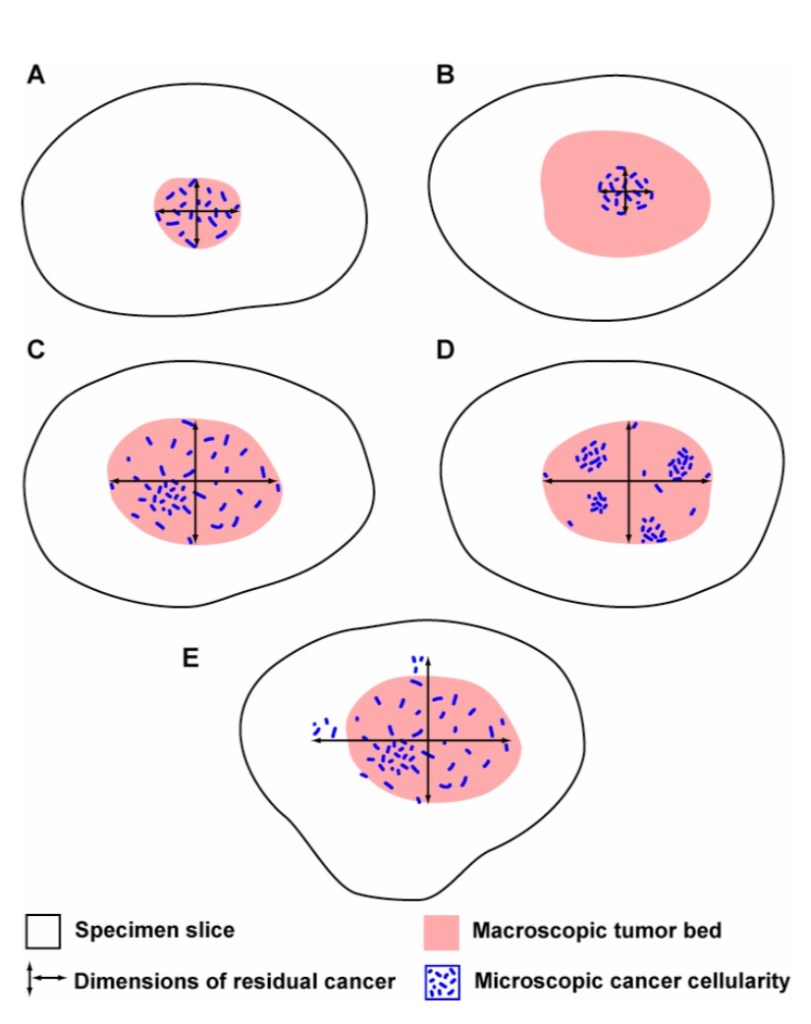
This approach accounts for differences in the concentration and distribution of residual cancer within a tumor bed. In the illustration above, the estimated % CA in example A would be high (in a small area), whereas the estimated % CA for examples C and D would be lower (in a larger area). In examples C and D, the estimated % CA would likely be similar, even though the distribution of cancer within the residual tumor bed is different in those two examples.



- It is recommended to repeat ER, PR, and HER2 on invasive TNBC after neoadjuvant therapy
- Distant metastasis in patient with residual disease after NAC:
- Factors associated with increased distant metastatic rate:
- Positive pathologic LN status
- Lymphovascular space invasion (LVSI)
- Increasing clinical T and N stage
- Multifocality
- Extranodal extension
- Factors associated with increased distant metastatic rate:


