👉Patients with small bowel carcinoids often present with a mesenteric mass without an imageable small bowel primary tumor.
- The differential diagnosis of an isolated mesenteric tumor includes:
- Lymphoma
- Desmoid tumor
- Reactive lymphadenopathy:
- From an inflammatory process
- Mesenteric peritoneal implant:
- From an abdominal malignancy
- Small bowel carcinoid
- Desmoid tumors:
- Often have a spiculated appearance on CT
- In carcinoid tumors with associated mesenteric masses:
- The relationship to the major mesenteric vessels should be assessed:
- As nodal carcinoid metastases:
- Can be unresectable:
- If they involve the root of the mesentery
- Can be unresectable:
- As nodal carcinoid metastases:
- The relationship to the major mesenteric vessels should be assessed:
- Patients with mesenteric masses should undergo:
- Biochemical testing for carcinoid:
- Serum chromogranin A
- Urine 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid [5-HIAA])
- Endoscopy:
- If the small bowel associated with the mesenteric mass is endoscopically accessible
- Small bowel enterography (CT or MRI):
- Can occasionally identify a previously occult primary small bowel tumor
- Biochemical testing for carcinoid:
Chromogranin A
- Chromogranins are peptides:
- Released from neuroendocrine cells:
- Vary day to day and with food intake
- Released from neuroendocrine cells:
- Depending on the threshold used:
- The sensitivity approaches 95%
- The specificity is low (55%):
- Given the high rate of false positivity:
- As it is elevated in multiple other conditions, including:
- Endocrine diseases
- Inflammatory conditions
- Proton pump inhibitor use
- As it is elevated in multiple other conditions, including:
- Given the high rate of false positivity:
5-HIAA
- 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA):
- Is the end product of serotonin metabolism:
- It is excreted in the urine
- Is the end product of serotonin metabolism:
- Twenty-four-hour urinary excretion of 5-HIAA:
- Can be elevated:
- In patients with carcinoid tumors
- It is most useful in patients:
- With carcinoid syndrome:
- Where it has high (90%) sensitivity and specificity
- With carcinoid syndrome:
- In patients with carcinoid tumors:
- Without carcinoid syndrome:
- The sensitivity is lower (~ 70%) even when using a low-level 5-HIAA cutoff
- Without carcinoid syndrome:
- Can be elevated:
- Foods containing high levels of tryptophan or serotonin and certain drugs:
- Can result in false positive values
CT
- Small bowel carcinoid tumors:
- Are often small (less than 2 cm median size):
- And are thus difficult to identify by cross-sectional imaging
- Are often small (less than 2 cm median size):
- Given the hypervascularity of these tumors:
- Arterial phase:
- May improve visibility
- Arterial phase:
- More commonly:
- CT imaging reveals:
- Mesenteric or hepatic metastases:
- Without a small bowel mass
- Mesenteric or hepatic metastases:
- CT imaging reveals:
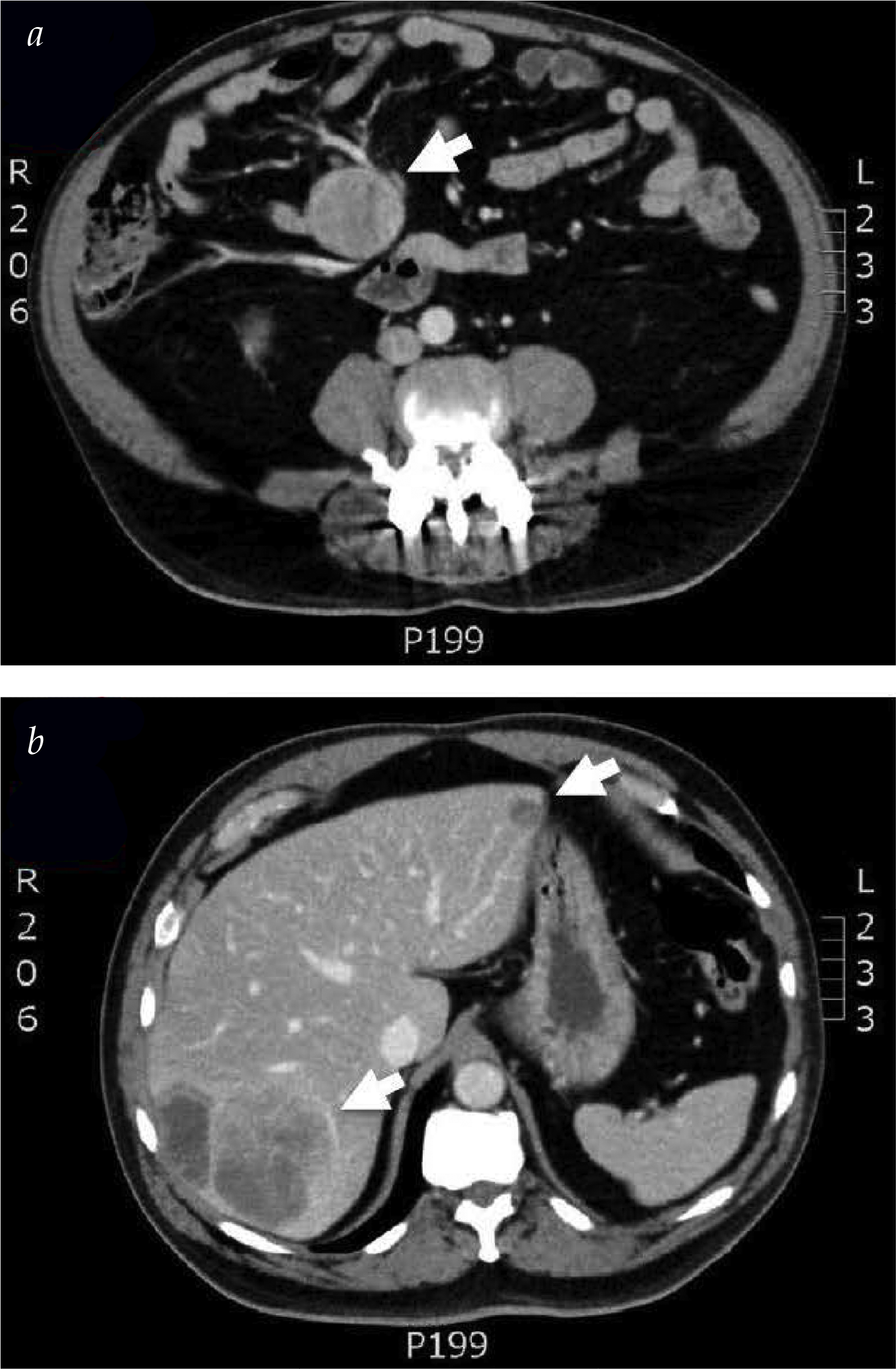
- The classic CT appearance demonstrates:
- A “spokes in a wheel” pattern:
- With a mesenteric nodal mass (wheel)
- With radiating desmoplastic fibrosis
- The occult primary small bowel carcinoid tumor:
- Is often in the bowel adjacent to the nodal metastases:
- And may manifest with radiographic signs of:
- A partial small bowel obstruction
- And may manifest with radiographic signs of:
- Is often in the bowel adjacent to the nodal metastases:
- A “spokes in a wheel” pattern:
- Enterography (CT or MR):
- May have higher sensitivity in detection small bowel carcinoids:
- But is not universally available and is understudied
- CT imaging:
- Often underestimates the extent:
- Of mesenteric, peritoneal, and hepatic metastases
- Often underestimates the extent:
- May have higher sensitivity in detection small bowel carcinoids:
OctreoScan
- Indium-111 pentetreotide (OctreoScan):
- Exploits the presence of:
- Somatostatin receptors on carcinoid tumor cells:
- Unlike high-grade neuroendocrine:
- Low-grade carcinoid tumors:
- Express:
- High levels of somatostatin receptors
- Express:
- Low-grade carcinoid tumors:
- Unlike high-grade neuroendocrine:
- Somatostatin receptors on carcinoid tumor cells:
- Exploits the presence of:
- Octreotide scans:
- Can allow for metastatic assessment and can predict response to somatostatin analogue therapy
- However:
- The spatial resolution and sensitivity of small carcinoid tumor detection:
- Is limited
- The spatial resolution and sensitivity of small carcinoid tumor detection:
- However:
- Can allow for metastatic assessment and can predict response to somatostatin analogue therapy
- Functional PET/CT (i.e., gallium-68 dotatate) scans:
- Offer improved sensitivity and resolution:
- And are preferred where available
- Offer improved sensitivity and resolution:
ENDOSCOPY
- Similar to small bowel adenocarcinomas:
- Small bowel carcinoids must be in an endoscopically accessible location to be visualized by endoscopy
- Because they are often in the distal most 60 cm of the terminal ileum:
- Colonoscopy or retrograde enteroscopy:
- Can often reach these tumors
- Colonoscopy or retrograde enteroscopy:
- Endoscopic assessment allows opportunities to:
- Biopsy and tattoo the lesion for identification during resection
#Arrangoiz #SurgicalOncologist #CancerSurgeon #Teacher #Surgeon #SmallBowelTumors #Carcinoids
