👉The pharyngeal muscles are a group of muscles that form the pharynx, which is posterior to the oral cavity, determining the shape of its lumen, and affecting its sound properties as the primary resonating cavity.
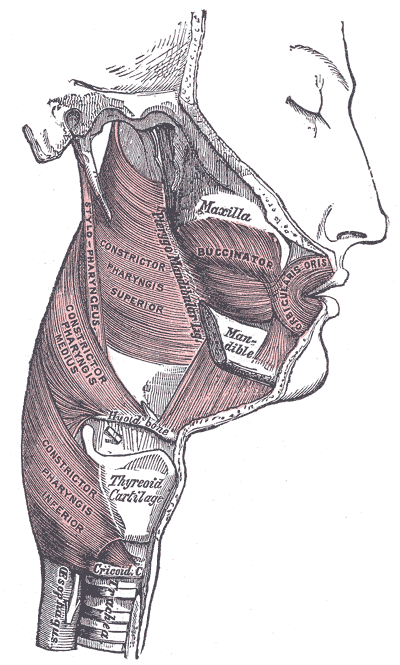
👉The pharyngeal musculature (involuntary skeletal muscles) function is to push the food bolus into the esophagus.
👉There are two muscular layers of the pharynx: the outer circular layer and the inner longitudinal layer.
👉The outer circular layer includes:
- Inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscle:
- Located in the laryngopharynx
- It has two components:
- Superior component (thyropharyngeus):
- Has oblique fibres that attach to the thyroid cartilage.
- Inferior component (cricopharyngeus):
- Has horizontal fibres that attach to the cricoid cartilage.
- Superior component (thyropharyngeus):
- Inserts posteriorly into the midline fibrous pharyngeal raphe
- Middle pharyngeal constrictor muscle:
- Located in the laryngopharynx
- Originates from the stylohyoid ligament and the horns of the hyoid bone.
- Inserts posteriorly into the midline fibrous pharyngeal raphe
- Superior constrictor muscle:
- The uppermost pharyngeal constrictor
- It is located in the oropharynx
- Originates from the pterygomandibular ligament, alveolar process of mandible and medial pterygoid plate and pterygoid hamulus of the sphenoid bone
- Inserts posteriorly into to the pharyngeal tubercle of the occiput and the medial fibrous pharyngeal raphe
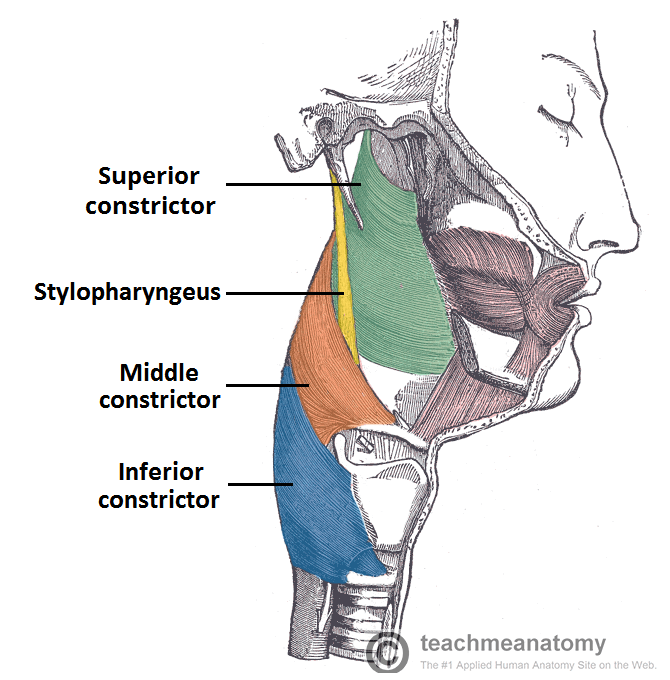
👉During swallowing, these muscles constrict to propel food bolus downwards (an involuntary process).
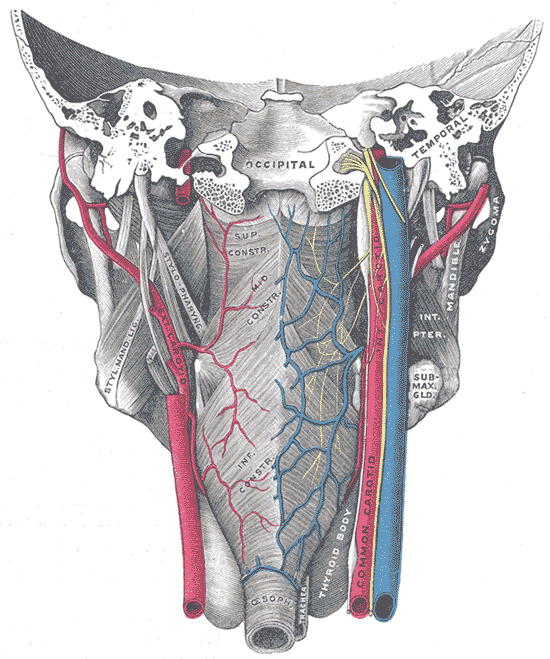
👉The inner longitudinal layer includes:
- Stylopharyngeus muscle:
- Arises from the styloid process of the temporal bone, inserts into the pharynx
- Unlike the other pharyngeal muscles:
- It is innervated by the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- Salpingopharyngeus muscle:
- Arises from the Eustachian tube, inserts into the pharynx
- Innervated by the vagus nerve (CN X)
- In addition to contributing to swallowing:
- It also opens the Eustachian tube to equalize the pressure in the middle ear
- Palatopharyngeus muscle:
- Arises from hard palate of the oral cavity, inserts into the pharynx
- Innervated by the vagus nerve (CN X)
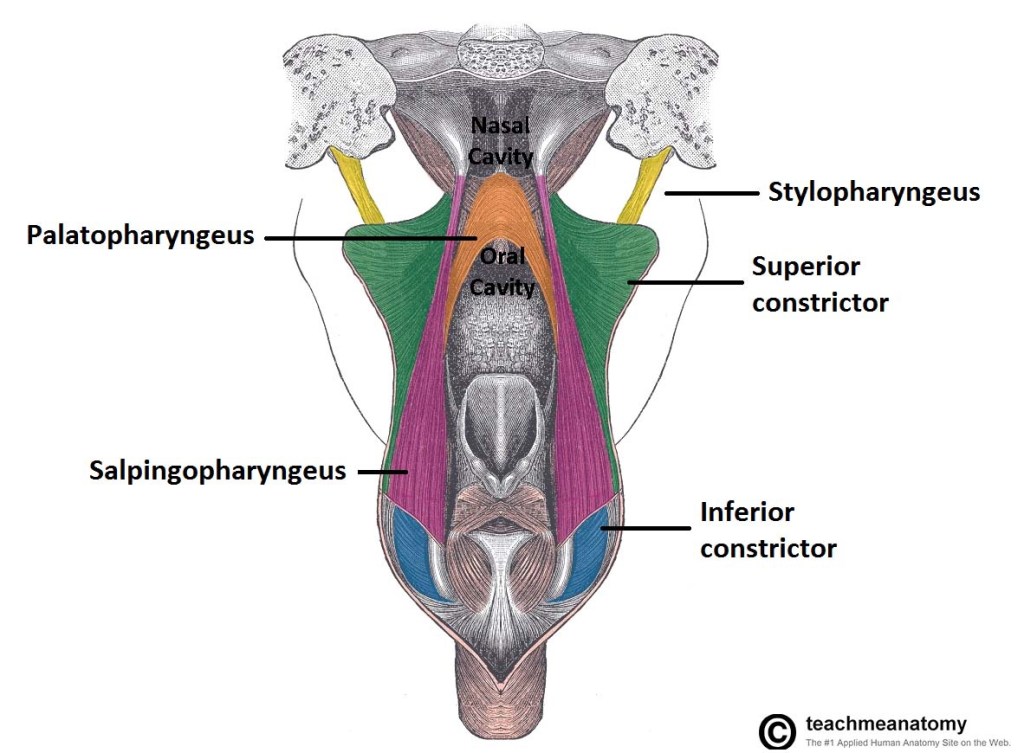
👉During swallowing, these muscles act to shorten and widen the pharynx.
👉They are innervated by the pharyngeal branch of the Vagus nerve (CN X) with the exception of the stylopharyngeus muscle which is innervated by the glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX).
#Arrangoiz #HeadandNeckSurgeon #CancerSurgeon #SurgicalOncologist
