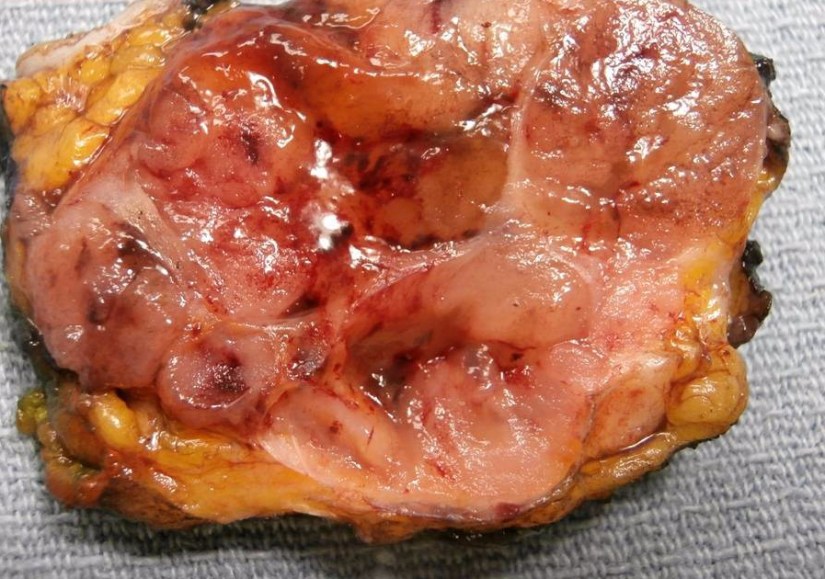
- Mucinous carcinoma of the breast (also known as colloid carcinoma) is a special type of breast cancer:Presenting with a large amount of extracellular mucin:That is associated with a relatively favorable prognosis
-
-
These tumors are uncommon:
-
In most series account for approximately 2% of invasive breast carcinomas
-
-
-
It is divided into two main subtypes based upon the quantification of cellularity:
-
The pure type:
-
In pure mucinous carcinomas:
-
Over 90% of the tumor is made up of malignant cell clusters floating in pools of mucin (see images)
-
-
-
-
-
Frequently, pure mucinous carcinomas can have posterior enhancement by ultrasound imaging:
-
That can lead to mistaking these lesions for cysts
-
-
-
-
Patients with pure mucinous carcinomas:
-
Tend to be postmenopausal:
-
Between the ages of 59 and 71 years:
-
-
-
-
-
-
But it can occasionally occur in patients who are younger than age 40 years:
-
-
-
-
-
-
The incidence of mucinous breast cancer in women under 35 years of age is less than 1%
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
The mixed type:
-
-
Tumors in which 50% to 90% of the mass is composed of malignant cell clusters floating in mucin are considered to be a mixed NOS and mucinous category:
-
-
Mixed mucinous carcinomas show a less distinct margin, a higher grade, and more mitotically active cytology
-
-
Their clinicopathologic features:
-
Are similar to those of invasive ductal carcinoma, NOS type
-
-
Some mucinous breast carcinomas (mainly mixed type) are associated with lobular or ductal neoplasia (in situ or invasive) and some have neuroendocrine differentiation:
-
Mucinous breast carcinoma associated with lobular neoplasia components:
-
Seems to be a biologically distinct subset that frequently shows decreased cell to cell adhesion, loss of cell polarity molecules and lack of neuroendocrine differentiation:
-
-
Also in this subset of tumors, the neoplastic cells with signet-ring features are most likely to be found
-
-
-
-
-
- Mucinous breast cancer is a slow-growing neoplasm:
-
-
With an estimated growth rate of one third of invasive breast cancer no special type
-
-
-
This malignancy also shows:
-
Fewer axillary lymph node metastases
-
-
-
Conventional, pure mucinous carcinomas:
-
Exhibit a rate of metastasis of less than 15%
-
-
Current studies have shown that a subset of patients diagnosed with mucinous carcinoma:
-
Do not manifest such favorable outcomes:
-
-
-
-
Some authors suggested that specific subtypes of pure mucinous carcinoma :
-
-
-
-
Those with a micropapillary pattern demonstrate significantly worse prognosis:
-
-
-
-
In one study more than half of the patients with this particular type of pattern were found to have vascular invasion and synchronous axillary lymph nodes
-
-
-
-
- A subset of mucinous breast carcinomas shows neuroendocrine differentiation:
-
-
Defined by cytoplasmic argyrophilia or immunoreactivity to markers such as:
-
-
Synaptophysin
-
-
-
Chromogranin
-
-
-
Neuronal specific enolase
-
-
-
-
Although in one study neuroendocrine differentiation:
-
Was associated with a favorable histology and a good outcome others did not find this association
-
-
Rodrigo Arrangoiz MS, MD, FACS a surgical oncologist and is a member of Mount Sinai Medical Center in Miami:
-
He is an expert in the management of breast cancer:
-
If you have any questions about breast cancer statistics please fill free to ask Dr. Arrangoiz
-
Training:
• General surgery:
• Michigan State University:
• 2004 al 2010
• Surgical Oncology / Head and Neck Surgery / Endocrine Surgery:
• Fox Chase Cancer Center (Filadelfia):
• 2010 al 2012
• Masters in Science (Clinical research for health professionals):
• Drexel University (Filadelfia):
• 2010 al 2012
• Surgical Oncology / Head and Neck Surgery / Endocrine Surgery:
• IFHNOS / Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center:
• 2014 al 2016