- The INSEMA trial:
- Citation:
- Reimer T, et al. New England Journal of Medicine, 2024/2025 (INSEMA Investigators).
- Citation:
- According to a study published in The New England Journal of Medicine:
- In this trial involving patients with clinically node-negative, T1 or T2 invasive breast cancer (90% with clinical T1 cancer and 79% with pathological T1 cancer):
- Omission of surgical axillary staging was noninferior to sentinel-lymph-node biopsy:
- After a median follow-up of 6 years
- Omission of surgical axillary staging was noninferior to sentinel-lymph-node biopsy:
- In this trial involving patients with clinically node-negative, T1 or T2 invasive breast cancer (90% with clinical T1 cancer and 79% with pathological T1 cancer):
- The trial also demonstrated that omission of SLNB resulted in:
- Lower rates of lymphedema
- Better arm mobility
- Less pain with arm or shoulder movement compared to SLNB:
- As confirmed by both clinical and patient-reported outcomes
- However, a slightly higher – but still low – rate of axillary recurrence was observed in the omission group:
- 1.0% vs. 0.3%:
- With no impact on overall survival
- 1.0% vs. 0.3%:
- These findings support the safety of omitting SLNB in carefully selected patients with early-stage, clinically node-negative breast cancer:
- Particularly those with favorable tumor biology:
- When the absence of nodal status will not alter adjuvant therapy decisions
- Particularly those with favorable tumor biology:
- The INSEMA trial (Intergroup‑Sentinel‑Mamma, often abbreviated “INSEMA”):
- A large European randomized study (5,500+ patients):
- Evaluating whether sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) can be safely omitted in selected patients with early-stage breast cancer
- A large European randomized study (5,500+ patients):
- Background and Design:
- Population:
- Clinically node-negative invasive breast cancer (cT1 to cT2, ≤ 5 cm), mostly hormone receptor–positive, HER2-negative tumors
- Patients candidates for breast‑conserving surgery and whole‑breast radiation
- All had negative axilla by clinical exam:
- Most centers used axillary ultrasound (AUS) as standard triage
- Trial Type:
- Prospective, randomized non‑inferiority study:
- Germany and Austria; 2015 to 2019
- Randomized in a 4 : 1 ratio:
- ~ 962 patients omitted SLNB versus ~ 3,896 who underwent standard SLNB
- Primary Endpoint:
- 5‑year invasive disease–free survival (iDFS):
- With non‑inferiority margin HR ≤ 1.271 and lower bound ≥ 85% iDFS
- 5‑year invasive disease–free survival (iDFS):
- Prospective, randomized non‑inferiority study:
- Population:
- Key Results (Median Follow‑up ≈ 73.6 months ≈ 6 years):
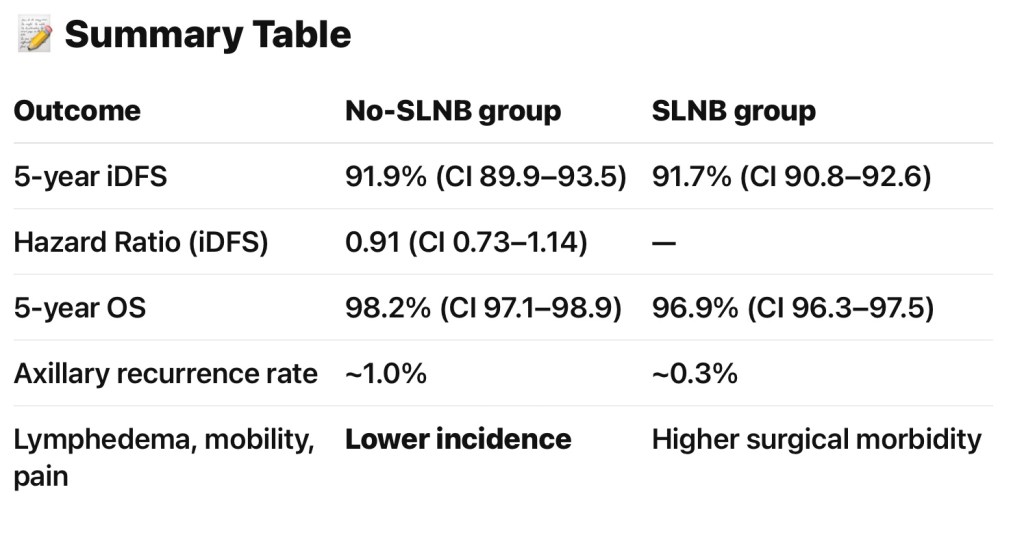
- Invasive Disease‑Free Survival (iDFS):
- No‑SLNB group:
- 5‑year iDFS ≈ 91.9% (95% CI: 89.9–93.5)
- SLNB group:
- 91.7% (95% CI: 90.8–92.6)
- Hazard Ratio:
- 0.91 (95% CI: 0.73–1.14), within non‑inferiority margin
- No‑SLNB group:
- Overall Survival (OS):
- No‑SLNB group:
- 98.2% (95% CI: 97.1–98.9)
- SLNB group:
- 96.9% (95% CI: 96.3–97.5)
- No‑SLNB group:
- Axillary Recurrence:
- Slightly higher in no‑SLNB group:
- ≈ 1.0% vs. ≈ 0.3%:
- But still very low clinically
- ≈ 1.0% vs. ≈ 0.3%:
- Slightly higher in no‑SLNB group:
- Invasive Disease‑Free Survival (iDFS):
- Secondary Outcomes:
- Quality of Life and Morbidity:
- Lower rates of lymphedema, better arm mobility, and less pain with arm / shoulder movement in the no‑SLNB group
- Patient‑reported outcomes consistently favored omission:
- Better arm symptom scores (BRAS) and overall quality of life scales (EORTC)
- Quality of Life and Morbidity:
- Clinical Implications:
- Omitting SLNB appears safe and non‑inferior for iDFS and OS:
- In carefully selected cN0 patients undergoing breast‑conserving therapy
- Best suited for:
- ≥ 50‑year‑old patients with low-risk tumors:
- ≤ 2 cm, grade 1 to grade 2, HR-positive, HER2-negative
- ≥ 50‑year‑old patients with low-risk tumors:
- Underrepresented groups (younger, grade 3, HER2‑positive or larger tumors):
- Were under‑powered for definitive recommendations
- Omitting SLNB appears safe and non‑inferior for iDFS and OS:
- Trial required whole‑breast radiation:
- No partial‑breast or omission of radiation was allowed, limiting generalizability
- Although non‑SLNB led to slightly higher axillary recurrence (1% vs 0.3%):
- The absolute rates remained extremely low (< 1%), with meaningful improvements in arm morbidity and quality of life
- Limitations and Cautions:
- Under‑powered subgroups:
- T2 tumors, younger patients, grade 3, or HER2+ disease:
- Had low representation and thus results may not apply
- T2 tumors, younger patients, grade 3, or HER2+ disease:
- No SLNB omission in the context of mastectomy, neoadjuvant therapy, or partial breast radiation:
- These settings were excluded
- Patient selection remains critical:
- Omitting nodal staging may impact systemic therapy decisions:
- Chemotherapy, genomic testing
- Omitting nodal staging may impact systemic therapy decisions:
- Under‑powered subgroups:
- The INSEMA trial:
- Demonstrates that in clinically node-negative women with early-stage, low-risk invasive breast cancer:
- Who are undergoing breast-conserving therapy with whole breast radiation:
- Omitting sentinel lymph node biopsy is non‑inferior for disease‑free and overall survival:
- While significantly reducing lymphedema risk and improving arm function and patient quality of life
- Omitting sentinel lymph node biopsy is non‑inferior for disease‑free and overall survival:
- Who are undergoing breast-conserving therapy with whole breast radiation:
- This de‑escalation strategy is particularly appropriate for:
- Patients over age 50 with:
- T1, grade 1 to grade 2, hormone receptor‑positive / HER2‑negative tumors
- However, broader application to younger patients, higher‑risk tumors, or non‑lumpectomy contexts should be approached with caution and discussed in a multidisciplinary setting
- Patients over age 50 with:
- Demonstrates that in clinically node-negative women with early-stage, low-risk invasive breast cancer:
- References:
- Axillary Surgery in Breast Cancer — Primary Results of the INSEMA Trial. Reimer T, Stachs A, Veselinovic K, et al. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2025;392(11):1051-1064. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2412063.
- Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy Omission in Early-Stage Breast Cancer: Current Evidence and Clinical Practice. Huang T, Wang W, Sun X. Frontiers in Oncology. 2025;15:1598730. doi:10.3389/fonc.2025.1598730.
- Patient-Reported Outcomes for the Intergroup Sentinel Mamma Study (INSEMA): A Randomised Trial With Persistent Impact of Axillary Surgery on Arm and Breast Symptoms in Patients With Early Breast Cancer. Reimer T, Stachs A, Veselinovic K, et al. EClinicalMedicine. 2023;55:101756. doi:10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101756.
- Axillary Surgery in Breast Cancer — Primary Results of the INSEMA Trial. Reimer T, Stachs A, Veselinovic K, et al. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2024;. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa2412063.