- Non-invasive follicular thyroid neoplasm with papillary-like nuclear features:
- NIFTP is the pathological definition of a type of noninvasive follicular cell-derived thyroid neoplas:
- That was first described in 2016
- This topic post-dated the 2015 ATA thyroid nodule and DTC guidelines:
- But a subsequent ATA task force statement in 2017 supported adoption of the NIFTP nomenclature for this entity
- In 2017, NIFTP were classified as a distinct category in the revised WHO Classification of Tumors of Endocrine Organs:
- Corresponding to a neoplasm with very low malignant potential
- NIFTP:
- Comprise approximately 2.1% to 9.6% of follicular cell derived thyroid neoplasms;
- With relatively lower incidence in Asia than in North America and Europe
- Comprise approximately 2.1% to 9.6% of follicular cell derived thyroid neoplasms;
- NIFTP:
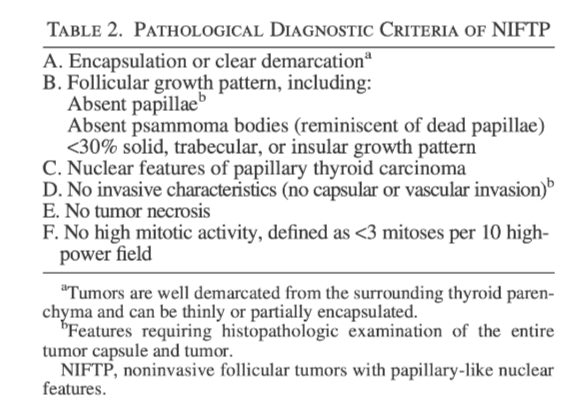
- Are characterized by validated histological inclusion and exclusion features (Table):
- The original NIFTP validation study excluded tumors:
- Measuring ≤ 1 cm
- Those with oncocytic features
- The original NIFTP validation study excluded tumors:
- However, as subsequent literature has shown that tumors measuring ≤ 1 cm (micro-NIFTPs) or with oncocytic features (oncocytic-NIFTPs):
- Demonstrate similar clinical behavior to those of original NIFTP these features also are included in the tumor’s current pathological definition
- Are characterized by validated histological inclusion and exclusion features (Table):
- The initial definition of NIFTP had required the presence of < 1% papillae:
- But subsequent experience has shown this feature can be associated with:
- Lymph node metastases:
- Therefore, the diagnostic criteria have been revised to require that papillae are absent
- Lymph node metastases:
- But subsequent experience has shown this feature can be associated with:
- It is recommended to carefully examine the entire tumor capsule interface and tumor:
- To exclude the possibility of invasive features and presence of papillae
- NIFTPs:
- Often coexist with one or more NIFTPs or other thyroid malignancies in the ipsilateral or contralateral lobes.
- Studies assessing the molecular profile of NIFTPs:
- Have shown them to be clonal neoplasms
- Molecular alterations are present in approximately 78% of cases:
- With approximately 30% to 54% of NIFTP tumors:
- Harboring a RAS mutation:
- NRAS mutations most common:
- Followed by HRAS and rarely KRAS mutations
- NRAS mutations most common:
- However, the NRAS mutations seen in NIFTPs may also be identified in FTCs and IEFVPTC:
- Therefore, they are nonspecific
- Harboring a RAS mutation:
- A small subset of NIFTP cases have been shown to harbor:
- PAX8::PPARc fusions
- THADA fusions
- BRAF K601E mutations
- Some studies also have explored miRNA expression in NIFTP cases:
- Demonstrating that two mi-RNAs (miR-10a05p and miR-320e):
- Can effectively discriminate between NIFTP and the infiltrative follicular variant of PTC:
- Further studies are required to validate these findings
- Can effectively discriminate between NIFTP and the infiltrative follicular variant of PTC:
- Demonstrating that two mi-RNAs (miR-10a05p and miR-320e):
- With approximately 30% to 54% of NIFTP tumors:
- While NIFTPs are characterized by:
- A follicular growth pattern and nuclear features of PTC:
- They are associated with extremely low malignant potential
- Several multiinstitutional series (largest sample, n = 363), including several that reclassified DTCs as NIFTP upon retrospective analyses:
- Have mostly reported zero risk of disease persistence / recurrence:
- Over a mean or median follow-up of up to 11.8 years
- Have mostly reported zero risk of disease persistence / recurrence:
- Lymph node metastases:
- Have been seen in < 5% of the total cohort and in only a few series
- Only one retrospective analysis of 102 cases showed the presence of distant metastases (to the lungs) in one case:
- Although this study was limited by incomplete follow-up (80%) and a high proportion of patients who received more aggressive care (total thyroidectomy and radioiodine ablation)
- A follicular growth pattern and nuclear features of PTC:
- At present, there are no available data comparing the clinical benefits and harms of various short- and long-term monitoring strategies in patients with NIFTP tumors
- NIFTP is the pathological definition of a type of noninvasive follicular cell-derived thyroid neoplas: