- ThyroSeq® test results refine cancer probability in thyroid nodules with indeterminate cytology, informing the most appropriate management of these patients
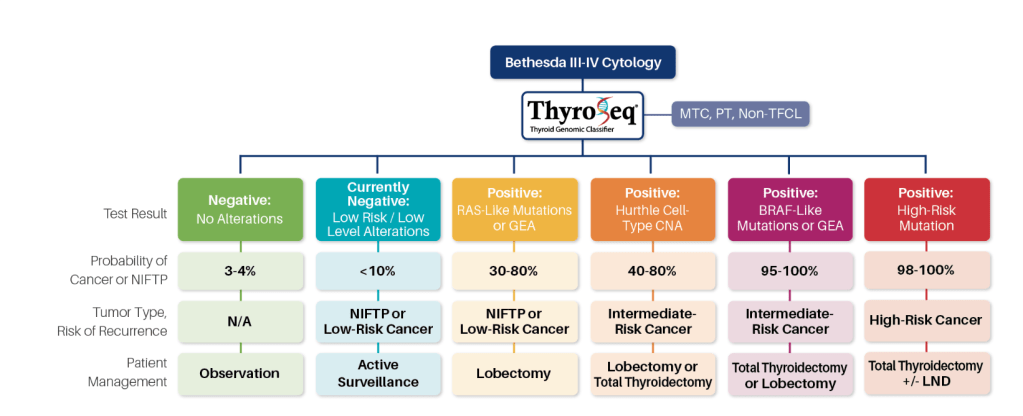
- Negative Results:
- According to NCCN guidelines, if molecular testing, in conjunction with clinical and ultrasound features, predicts a risk of cancer comparable to the risk of malignancy seen in a benign FNA cytology (roughly 5% or less):
- Active surveillance can be considered
- Therefore, in those clinical situations where the pretest probability of cancer in nodules with Bethesda III and IV cytology is less than 44%:
- A negative ThyroSeq test results would confer the cancer probability of 5% or less:
- Justifying observation in lieu of surgical management in appropriately selected cases
- Because the probability of cancer in such nodules is comparable to benign FNA cytology, the management of patients may follow the recommendations for nodules with benign cytology:
- Which, based on the 2015 ATA guidelines, should be determined based on ultrasound (US) pattern (Recommendation #23)
- A negative ThyroSeq test results would confer the cancer probability of 5% or less:
- In nodules with Bethesda V cytology and negative ThyroSeq result:
- The residual cancer risk of ~20% does not allow to avoid surgical management:
- Thyroid lobectomy may be sufficient initial treatment for many of these patients
- The residual cancer risk of ~20% does not allow to avoid surgical management:
- According to NCCN guidelines, if molecular testing, in conjunction with clinical and ultrasound features, predicts a risk of cancer comparable to the risk of malignancy seen in a benign FNA cytology (roughly 5% or less):
- Currently Negative Results:
- Test results are reported as currently negative:
- When the sample is found positive for a low risk and / or low-level gene mutation, DNA copy number alterations (CNA) or gene expression alterations (GEA) that alone is not sufficient for full cancer development
- Although at the time of sampling most of these nodules are benign:
- Some of them may undergo clonal expansion and acquire additional mutations
- In the absence of suspicious US features or other clinical risk factors:
- Many of these patients are likely to benefit from active surveillance with repeat of clinical exam and potentially FNA and molecular testing in 1 year
- Test results are reported as currently negative:
- Positive RAS-Like or GEA Results:
- ThyroSeq test positive for an isolated RAS mutation or RAS-like alteration (e.g. BRAF K601E mutation, THADA fusion, RAS-like GEA):
- Indicates that the nodule is a tumor (not hyperplasia) and predicts, depending on the specific alteration:
- A 30% to 80% probability of either a low-risk cancer or a pre-cancerous tumor, NIFTP
- Indicates that the nodule is a tumor (not hyperplasia) and predicts, depending on the specific alteration:
- Many of these nodules may be managed by therapeutic lobectomy:
- Which is currently recommended by the ATA guidelines for low-risk papillary and follicular carcinomas (Recommendation #35) and NIFTP
- ThyroSeq test positive for an isolated RAS mutation or RAS-like alteration (e.g. BRAF K601E mutation, THADA fusion, RAS-like GEA):
- Positive BRAF-Like of GEA Results:
- ThyroSeq test positive for an isolated BRAF V600E or BRAF V600E-like alteration (e.g. RET / PTC, BRAF fusions, BRAF V600E-like GEA):
- Confers a very high (greater than 95%) probability of cancer
- According to the ATA guidelines:
- BRAF-mutated unifocal intrathyroidal carcinoma less than 1 cm in size has low risk for recurrence:
- Therefore may be treated with thyroid lobectomy alone
- Whereas 1 cm to 4 cm BRAF-positive PTC is an intermediate-risk tumor:
- Where total thyroidectomy or lobectomy should be considered based on clinical and US findings
- BRAF-mutated unifocal intrathyroidal carcinoma less than 1 cm in size has low risk for recurrence:
- ThyroSeq test positive for an isolated BRAF V600E or BRAF V600E-like alteration (e.g. RET / PTC, BRAF fusions, BRAF V600E-like GEA):
- Postive Oncocytic Cell Type (formely Hurthle Cell Type) CNA Results:
- ThyroSeq test positive for isolated oncocytic cell type / Hürthle cell-type copy number alterations (CNA) confers, in different nodule size groups:
- A 40% to 80% probability of Hürthle Cell carcinoma:
- Whereas the rest of these nodules are benign Hurthle Cell adenomas
- A 40% to 80% probability of Hürthle Cell carcinoma:
- ThyroSeq test positive for isolated oncocytic cell type / Hürthle cell-type copy number alterations (CNA) confers, in different nodule size groups:
- Positive High Risk Mutations Results:
- ThyroSeq test positive for multiple high-risk mutations (e.g. BRAF V600E and TERT) confers a very high probability of cancer and predicts an increased risk of disease recurrence by the ATA guidelines and of tumor-related mortality
- Most of these patients would likely benefit from total thyroidectomy, with possible consideration for regional lymph node dissection if one of the mutations is BRAFV600E

