- During the fifth to sixth week of intrauterine development:
- The embryonic pharynx is marked:
- Externally by:
- Four branchial clefts of ectoderm origin
- Internally by:
- Five branchial pouches of endoderm origin
- Externally by:
- The embryonic pharynx is marked:
- The branchial apparatus:
- Is made up by the branchial clefts and branchial pouches:
- Together with the branchial arches of mesoderm origin:
- Found in between them
- Together with the branchial arches of mesoderm origin:
- This apparatus undergoes normal involution:
- Leaving behind some derivatives which include the thyroid gland, parathyroid glands, thymus, ultimobranchial body, Eustachian tube, middle ear, and external auditory canal
- Is made up by the branchial clefts and branchial pouches:
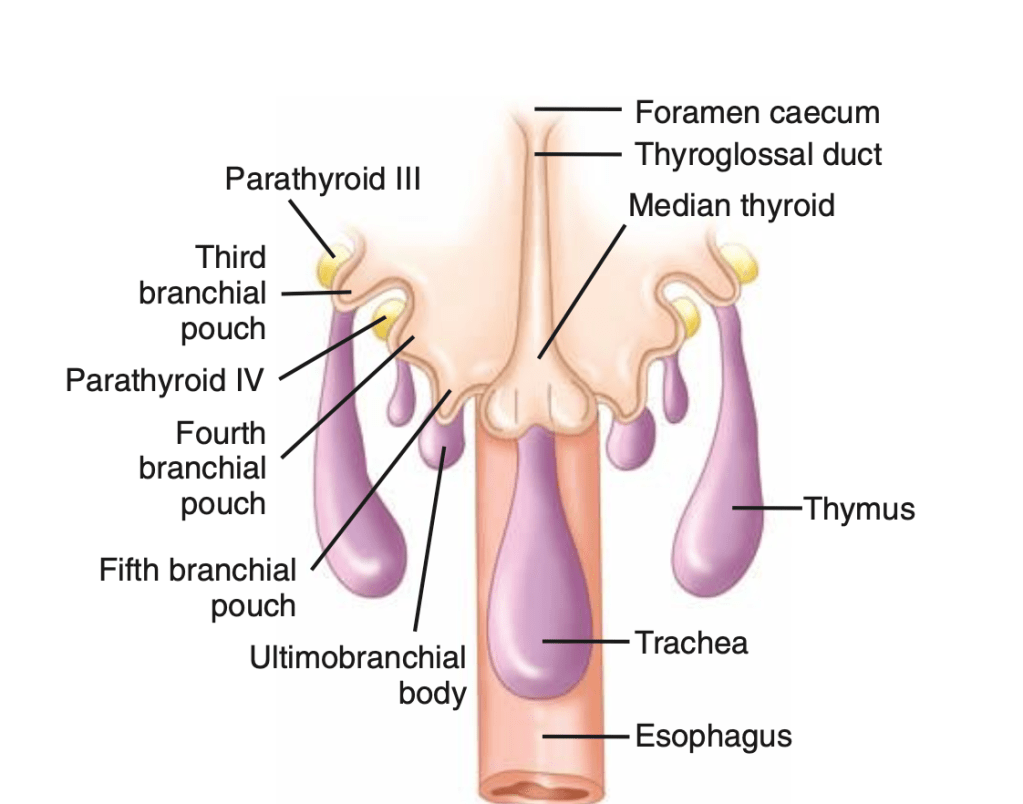
- The parathyroid glands:
- Develop as epithelial thickenings of the dorsal endoderm of the third and fourth branchial pouches
- The superior parathyroid glands:
- Are derived from the fourth branchial pouch:
- Which also gives rise to the thyroid gland
- Are derived from the fourth branchial pouch:
- The inferior parathyroid glands:
- Are derived from the third branchial pouch:
- Which also gives rise to the thymus
- Are derived from the third branchial pouch:
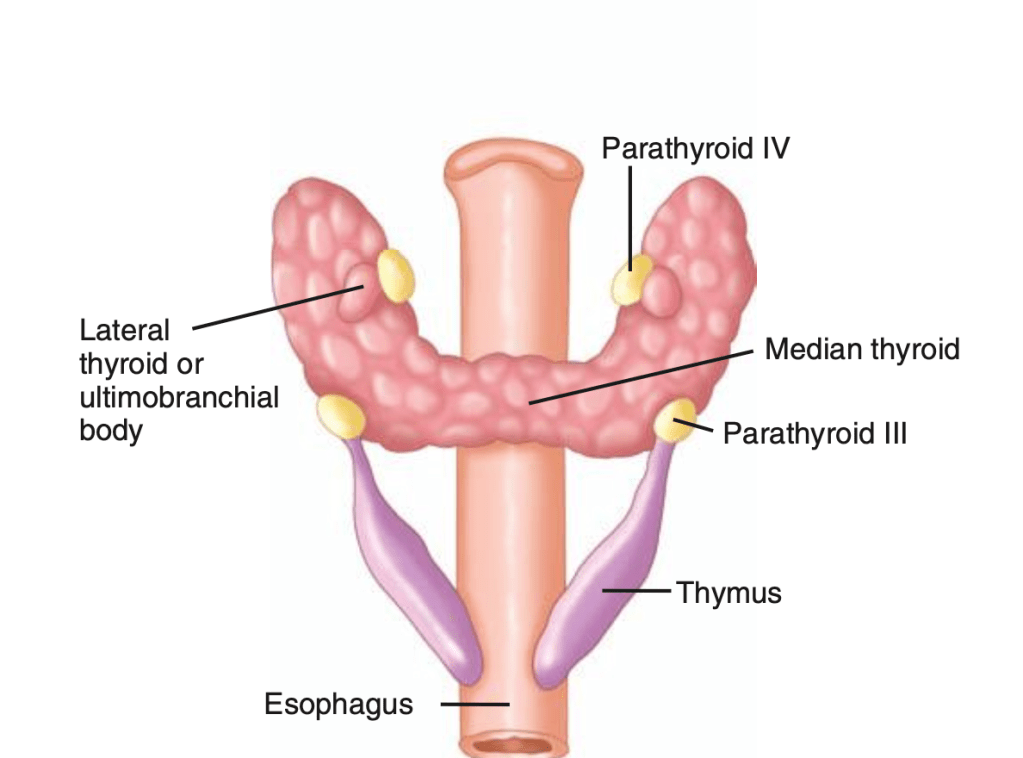
- The parathyroid glands:
- Remain intimately connected with their respective branchial pouch derivatives
- The normal anatomic location of the superior parathyroid glands:
- Is more constant than the inferior parathyroid glands:
- With 80% of the superior glands being found near the posterior aspect of the thyroid gland at the junction of the upper and middle portion of the thyroid lobes:
- At the level of the cricoid cartilage:
- Each gland with its own capsule of connective tissue
- At the level of the cricoid cartilage:
- With 80% of the superior glands being found near the posterior aspect of the thyroid gland at the junction of the upper and middle portion of the thyroid lobes:
- Roughly one percent of the superior parathyroid glands;
- May be found in the paraesophageal or retroesophageal space
- Enlarged superior glands may descend in the tracheoesophageal groove and come to lie below the inferior parathyroid glands
- Truly ectopic superior parathyroid glands:
- Are extremely rare:
- But may be localized to the middle or posterior mediastinum or in the aortopulmonary window
- Are extremely rare:
- Is more constant than the inferior parathyroid glands:
- During intrauterine development, the thymus and the inferior parathyroid glands migrate caudally in the neck:
- The most common location for the inferior parathyroid glands:
- Is within a distance of 1 cm from a point centered where the inferior thyroid artery and the recurrent laryngeal nerve (RLN) cross
- Approximately 15% to 50% of the inferior glands:
- Are found in the thymus
- The position of the inferior parathyroid glands:
- However, tends to be more variable:
- Due to their longer migratory route
- However, tends to be more variable:
- Undescended inferior glands:
- May be found near the skull base, angle of the mandible, or above the superior parathyroid glands along with an undescended thymus
- The most common location for the inferior parathyroid glands:
- The frequency of intrathyroidal glands:
- Is approximately 2%
- There are normally two pairs of parathyroid glands (inferior and superior)
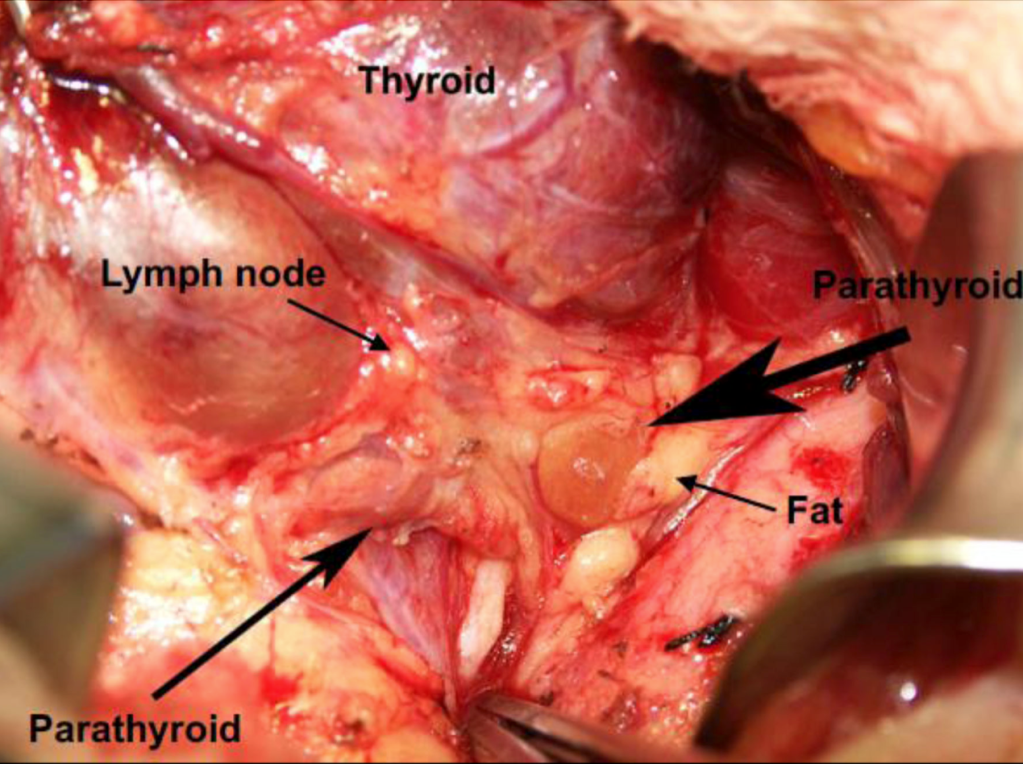
- The parathyroid gland:
- Is oval or bean-shaped (Figure)
- It typically measures 6 mm × 4 mm × 2 mm
- Weighs 40 mg to 60 mg
- The parathyroid gland:
- Most people have four parathyroid glands:
- Akerström et al, in a series of 503 autopsies:
- Identified four parathyroid glands in 84% of the cases
- Supernumerary glands were found in:
- 13% of the cases:
- Most commonly in the thymus
- In the literature, the incidence of supernumerary glands:
- Is anywhere between 3% and 13%
- 13% of the cases:
- Only in three percent of the cases less than four parathyroid glands are identified
- Akerström et al, in a series of 503 autopsies:
- The superior glands usually are dorsal to the RLN at the level of the cricoid cartilage:
- Whereas the inferior parathyroid glands are located ventral to the nerve