- LIBRETTO‑531:
- Design & Patient Population:
- Phase III, global, multicenter, open-label, randomized (2:1) trial (NCT04211337):
- Comparing selpercatinib (160 mg BID) to physician’s choice of cabozantinib or vandetanib:
- In MKI-naïve, progressive advanced /metastatic RET-mutant MTC patients
- Stratified by RET M918T mutation status and intended control arm MKI
- Crossover permitted from MKI arm to selpercatinib upon progression
- Comparing selpercatinib (160 mg BID) to physician’s choice of cabozantinib or vandetanib:
- Phase III, global, multicenter, open-label, randomized (2:1) trial (NCT04211337):
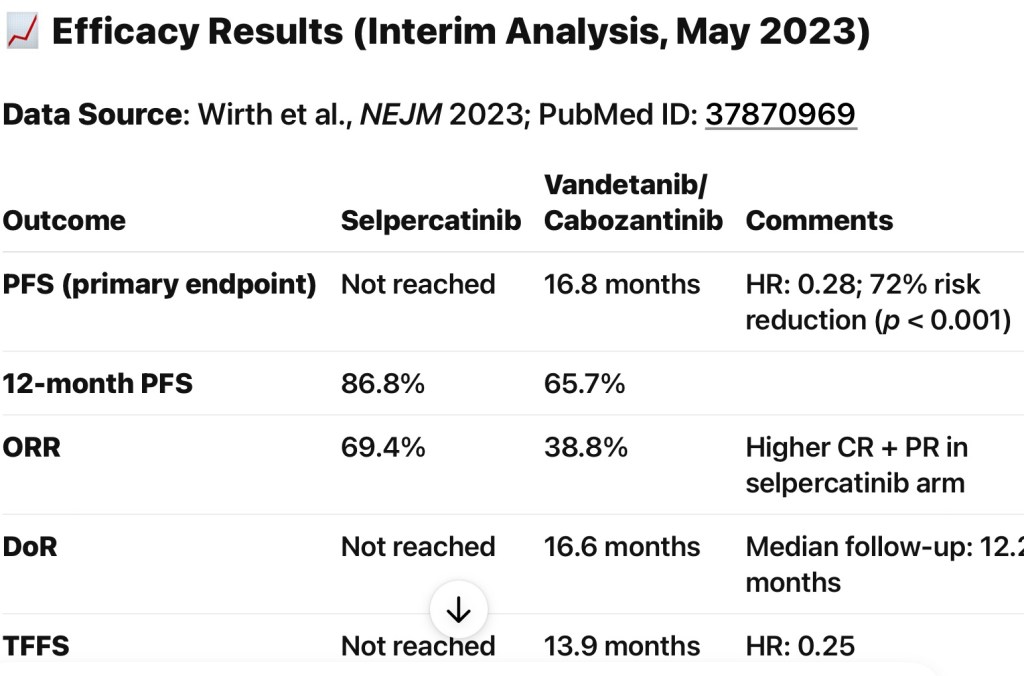
- Efficacy Results (Interim, ~ 12-months follow-up):
- Primary endpoint (PFS, RECIST v1.1):
- Selpercatinib:
- Median not reached
- MKI arm:
- 16.8 months (95% CI, 12.2–25.1); HR 0.28; P<0.001
- 12‑month PFS:
- 86.8% vs 65.7%
- Selpercatinib:
- Secondary endpoint (Treatment Failure-Free Survival – TFFS):
- Not reached vs 13.9 months in MKI arm; HR 0.25
- Overall Response Rate (ORR):
- 69.4% in selpercatinib group vs 38.8% in MKI group
- Safety-driven dose modifications:
- 38.9% with selpercatinib vs 77.3% with MKIs
- Discontinuations 4.7% vs 26.8%
- Primary endpoint (PFS, RECIST v1.1):
- Design & Patient Population:
- Safety & Patient-Reported Outcomes:
- Common ≥ 25% AEs:
- Hypertension, edema, dry mouth, fatigue, diarrhea
- Grade 3/4 laboratory abnormalities:
- Lymphopenia, elevated ALT / AST, electrolyte disturbances
- Patient-reported tolerability (FACT-GP5):
- Demonstrated robust reliability (ICC 0.80–0.85); high side-effect burden correlated with decreased functioning
- Mechanism of Action:
- Selpercatinib is a highly selective RET inhibitor, effective against both:
- RET point mutations (e.g., M918T in MTC)
- RET fusions (common in papillary thyroid carcinoma and NSCLC)
- High selectivity translates to less off-target toxicity compared to multikinase inhibitors (vandetanib/cabozantinib), which inhibit VEGFR, MET, etc.
- Selpercatinib is a highly selective RET inhibitor, effective against both:
- Guideline Endorsements:
- NCCN (2024) now includes selpercatinib as a Category 1 first-line option:
- For RET-mutant, progressive/unresectable MTC, alongside cabozantinib and vandetanib
- ATA Guidelines:
- Similarly endorse selective RET inhibitors as preferred agents for RET-driven MTC
- ESMO / European Consensus:
- Align with use in RET-mutant MTC post-MKI therapy
- NCCN (2024) now includes selpercatinib as a Category 1 first-line option:
- Regulatory Perspective:
- FDA granted traditional approval on September 27, 2024 for adults and pediatrics ≥ 2 years with advanced / metastatic RET-mutant MTC requirement systemic therapy
- Earlier accelerated approval received in 2020 for patients ≥ 12 years; expanded to ≥ 2 years with pediatric dosing in May 2024
- Clinical Implications for Head and Neck Oncology Teams:
- First-line therapy improvement:
- LIBRETTO‑531 is the first randomized trial demonstrating selpercatinib superiority over MKIs in efficacy and tolerability
- Reduced surgical urgency:
- Durable responses may defer or potentially downstage extra-thyroidal or metastatic disease, assisting in surgical planning
- Multidisciplinary coordination:
- Shared decision-making essential for selecting candidates, managing MTC lesion status, and monitoring biochemical markers (calcitonin, CEA)
- Monitoring & sequencing:
- Be vigilant for long-term tolerability needs, dose adjustments, and resistance (e.g., RET solvent-front mutations); TKIs sequencing should involve endocrine-oncology collaboration
- First-line therapy improvement:
- Recommended References for Further Reading:
- Primary LIBRETTO‑531 publication: NEJM (PubMed PMID: 37870969)
- Preceding phase I/II evidence: Wirth et al., N Engl J Med 2020 (LIBRETTO‑001)
- NCCN Thyroid Carcinoma Guidelines, v2.2024 .
FDA approval details for selpercatinib - Patient-reported outcomes analysis: Regnault et al., J Patient Rep Outcomes 2024
- Summary for Surgical Experts:
- Selpercatinib sets a new standard first-line systemic therapy in RET-mutant MTC, delivering superior tumor and nodal responses while maintaining patient quality-of-life
- Surgeons should integrate molecular profiling early, allowing neoadjuvant-like benefit of targeted therapy before considering resection or resection of metastatic deposits
- Long-term surgical planning may be increasingly influenced by TKI response and durability

- Clinical Implications for Surgeons and Oncologists:
- Preoperative:
- Patients with borderline resectable MTC may benefit from downstaging with selpercatinib
- Early molecular testing for RET mutations is essential
- Postoperative:
- Patients with biochemical persistence (calcitonin / CEA) or structural recurrence can receive selpercatinib earlier
- More favorable AE profile allows longer-term outpatient management
- Preoperative:
- References:
- Wirth LJ, et al. Selpercatinib vs Standard Therapy in RET-Mutant MTC. N Engl J Med. 2023;389(15):1344-1356. PMID: 37870969
NCCN Guidelines: Thyroid Carcinoma v2.2024. https://www.nccn.org - ATA Guidelines Update (Thyroid, 2022): Use of targeted therapy in RET-mutant disease
FDA Approval Summary: https://www.fda.gov/drugs - Drilon A, et al. Targeting RET-driven cancers with selpercatinib. Cancer Discov. 2020. PMID: 3221355
- Wirth LJ, et al. Selpercatinib vs Standard Therapy in RET-Mutant MTC. N Engl J Med. 2023;389(15):1344-1356. PMID: 37870969


