- Most patients have four parathyroid glands
- The superior glands usually are dorsal to the RLN at the level of the cricoid cartilage
- The inferior parathyroid glands are located ventral to the nerve
- Normal parathyroid glands are gray and semitransparent in newborns:
- But appear golden yellow to light brown in adults:
- Parathyroid color depends on cellularity, fat content, and vascularity
- Moreover, they often are embedded in and sometimes difficult to discern from surrounding fat
- But appear golden yellow to light brown in adults:
- There are normally two pairs of parathyroid glands (inferior and superior)
- The parathyroid gland is oval or bean-shaped (Figure)
- It typically measures 6 mm × 4 mm × 2 mm
- They weigh 40 mg to 60 mg
- Most people have four parathyroid glands:
- Akerström et al, in a series of 503 autopsies:
- Identified four parathyroid glands in 84% of the cases
- Supernumerary glands were found in 13% of the cases:
- Most commonly in the thymus
- In the literature, the incidence of supernumerary glands:
- Is anywhere between 3% and 13%
- Akerström et al, in a series of 503 autopsies:
- Only in three percent of the cases less than four parathyroid glands are identified
- The blood supply of the parathyroid glands:
- Is usually derived from branches of the inferior thyroid artery:
- Although branches of the superior thyroid artery can supply at least 10% to 45% of the superior parathyroid glands
- In a study of 354 autopsy specimens, Alverd, observed:
- That both the superior and inferior parathyroid glands derive their blood supply from the inferior thyroid artery:
- 86% on the right side and 77% from the left side
- That both the superior and inferior parathyroid glands derive their blood supply from the inferior thyroid artery:
- When the inferior thyroid artery was absent:
- Both the superior and inferior parathyroid glands were supplied by the superior thyroid artery
- Branches from the thyroidea ima, and vessels to the trachea, esophagus, larynx, and mediastinum:
- May also contribute to the irrigation of the parathyroid glands
- Is usually derived from branches of the inferior thyroid artery:
- Wang et al., in a study of 160 autopsy specimens:
- Showed that a low lying inferior parathyroid gland could be identified by following the vascular pedicle of the inferior thyroid artery
- The parathyroid glands drain ipsilaterally by the:
- Superior, middle, and inferior thyroid veins
- The innervation of the parathyroid glands:
- Occurs via the superior or middle cervical ganglia, or through a plexus in the fascia on the posterior aspect of the thyroid lobe
- Histologically, parathyroid glands are composed of:
- Chief cells and oxyphil cells arranged in trabeculae, within a stroma composed primarily of adipose cells (Figure)
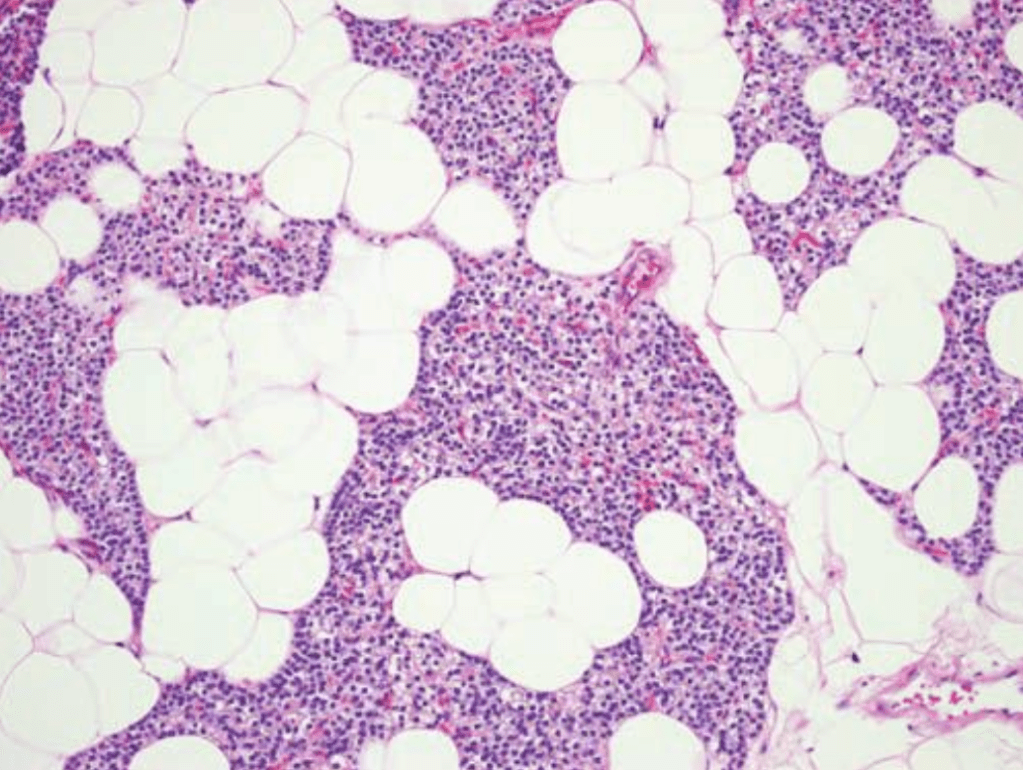
- The parathyroid glands of infants and children:
- Are composed mainly of chief cells:
- Which produce parathyroid hormone (PTH)
- Are composed mainly of chief cells:
- Acidophilic, mitochondria-rich oxyphil cellsL:
- Are derived from chief cells:
- Can be seen around puberty:
- They increase in numbers in adulthood
- Can be seen around puberty:
- Are derived from chief cells:
- A third group of cells, known as water-clear cells:
- Also are derived from chief cells
- Are present in small numbers, and are rich in glycogen
- Although most oxyphil and water-clear cells retain the ability to secrete PTH:
- Their functional significance is not known.

