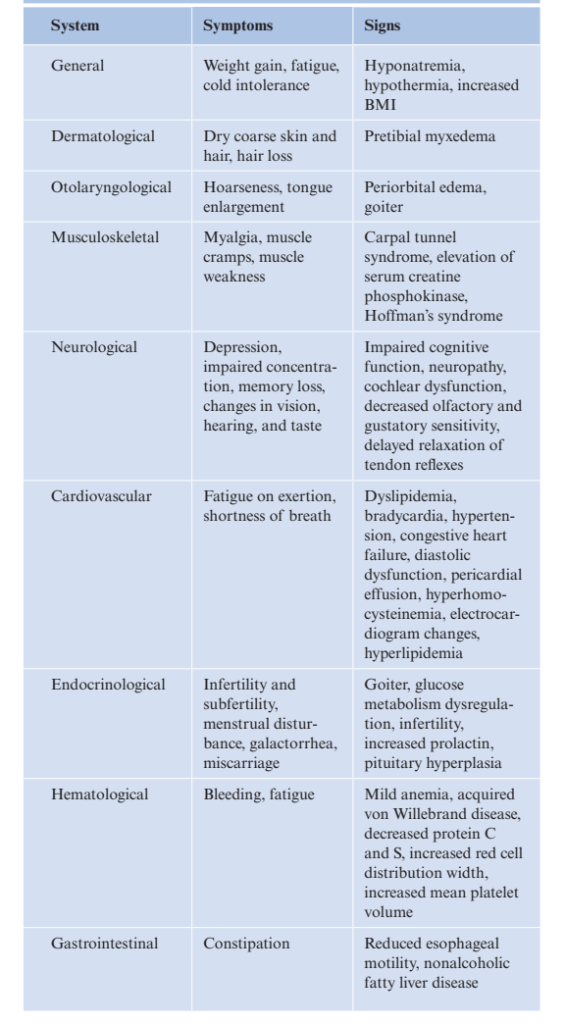
- Signs and Symptoms of Hypothyroidism:
- Commons signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism are mostly nonspecific, and some patients may not display any signs or symptoms
- Symptoms may be insidious, and in the elderly and middle-aged women:
- Nonspecific complaints may be interpreted as signs of normal aging or depression
- Symptoms of hypothyroidism depend on the degree and duration of the disease:
- But most frequently include:
- Weight gain
- Fatigue
- Constipation
- Menstrual irregularities / infertility
- But most frequently include:
- General signs and symptoms of hypothyroidism:
- Weight gain
- Fatigue
- Cold Intolerance
- Hyponatremia
- Hypothermia
- Increased body mass index
- Skin:
- Dry and coarse skin
- Dry and coarse hair
- Pretibial myxedema (non pitting edema)
- Hair loss
- Head and Neck:
- Hoarse voice
- Enlarged tongue
- Periorbital edema
- Goiter
- Gastrointestinal:
- Constipation
- Reduced esophageal motility
- Nonalcoholic fatty liver
- Musculoskeletal:
- Myalgia
- Muscle cramps
- Muscle weakness
- Carpel tunnel syndrome
- Elevation of serum creatine phosphokinase
- Hoffman’s syndrome:
- Rare form of hypothyroid myopathy:
- Characterized by pseudohypertrophy (increased muscle mass) and proximal muscle weakness:
- Particularly in the legs
- Characterized by pseudohypertrophy (increased muscle mass) and proximal muscle weakness:
- Rare form of hypothyroid myopathy:
- Nervous system:
- Depression
- Impaired concentration
- Memory loss
- Changes in vision, hearing, and taste
- Dementia
- Impaired congitive function
- Neurophathy
- Cochlear dysfunction
- Decreased gustartory and olfactory sensitivity
- Delayed relaxation of tendon reflexes
- Cardiovascular:
- Fatigue on exertion
- Shortness of breath
- Bradycardia
- Diastolic hypertension
- Dyslipidemia
- Electrocardiogram changes
- Hyperlipidemia
- Pericardial effusion
- Congestive heart failure
- Reproductive:
- Irregular menstrual periods
- Amenorrhea
- Galactorrhea:
- If accompiend by elevated prolactin levels
- Infertility
- Miscarriage
- Hematological:
- Bleeding
- Fatigue
- Mild anemia
- Acquired von Willebrand disease
- Decreased protein C and S
- Increased red blood cell distribution width
- Increased mean platelet volume
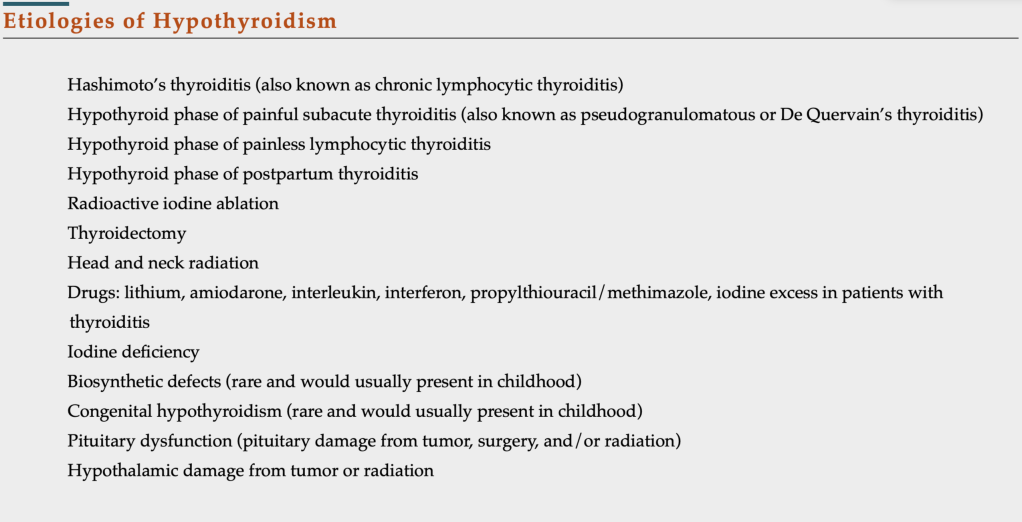
- Etiologies of Hypothyroidism:
- The most common etiologies of decreased serum thyroid hormone concentrations are those associated with primary hypothyroidism:
- Which is defined as underproduction of thyroid hormone at the thyroid gland
- Excluding postsurgical and postablative hypothyroidism:
- The most common cause of adult hypothyroidism worldwide is:
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis
- The most common cause of adult hypothyroidism worldwide is:
- Causes of hypothyroidism associated with secondary and tertiary disease:
- When hypothyroidism arises from pituitary and hypothalamic insults, respectively:
- Are much less common
- When hypothyroidism arises from pituitary and hypothalamic insults, respectively:
- The most common etiologies of decreased serum thyroid hormone concentrations are those associated with primary hypothyroidism:
- It is important that hypothyroidism arising from Hashimoto’s thyroiditis:
- Be distinguished from transient forms of hypothyroidism:
- Such as excess iodine exposure
- The hypothyroid phase of subacute thyroiditis
- Hypothyroidism arising from Hashimoto’s thyroiditis:
- Is an indication for lifelong thyroid hormone replacement:
- The transient forms of hypothyroidism may not necessarily require this
- Is an indication for lifelong thyroid hormone replacement:
- Be distinguished from transient forms of hypothyroidism:
- The most common forms of subacute thyroiditis are:
- Postpartum thyroiditis
- Painful subacute thyroiditis
- Painless subacute or silent thyroiditis
- All forms of subacute thyroiditis:
- Are characterized by the triphasic pattern of transient thyrotoxicosis (i.e., 1 to 3 months):
- Followed by transient hypothyroidism (i.e., lasting up to 6 months):
- With the eventual return to the euthyroid state:
- Although not all patients will experience all phases
- With the eventual return to the euthyroid state:
- Followed by transient hypothyroidism (i.e., lasting up to 6 months):
- Postpartum thyroiditis:
- Occurs in the few months after a:
- Miscarriage, therapeutic abortion, or delivery
- Occurs in the few months after a:
- Subacute painful thyroiditis:
- Is associated with:
- An enlarged and tender thyroid gland
- Variably presents with flulike symptoms:
- High fever, myalgia, and a high serum erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR)
- Is associated with:
- Painless or silent lymphocytic subacute thyroiditis:
- Is associated with an enlarged thyroid gland
- All three types of subacute thyroiditis:
- Can be diagnosed by a:
- Very low radioactive iodine uptake
- Can be diagnosed by a:
- In most cases, the hypothyroid phase of subacute thyroiditis does not require treatment with thyroid hormone replacement:
- Unless the patient is symptomatic or the hypothyroidism is biochemically severe
- Are characterized by the triphasic pattern of transient thyrotoxicosis (i.e., 1 to 3 months):

