- Medullary thyroid cancer (MTC):Accounts for approximately 1% to 2% of thyroid cancers in the United States.
- These tumors originate from:The neural crest derived parafollicular C-cells of the thyroid gland:Which produce calcitonin:Other secretory products made by the C-cells include:Carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA)
- Most MTCs occur sporadically (75%):But they are also found in hereditary syndromes (25% of the cases) such as:Multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) 2A
- MEN2A accounts for 95% of MEN2 cases:Is characterized by: MTC
- The familial forms are characterized by:Germline mutations in the RET proto-oncogene:Located on chromosome 10q 11.2:It encodes a single pass transmembrane receptor of the tyrosine kinase family
-
- RET is typically expressed in the cells of:The neural crest
- Approximately 50% of sporadic MTCs harbor somatic RET mutations
- 18% to 80% of sporadic MTC lacking somatic RET mutations have:Somatic mutations of:HRAS, KRAS, or rarely NRAS.
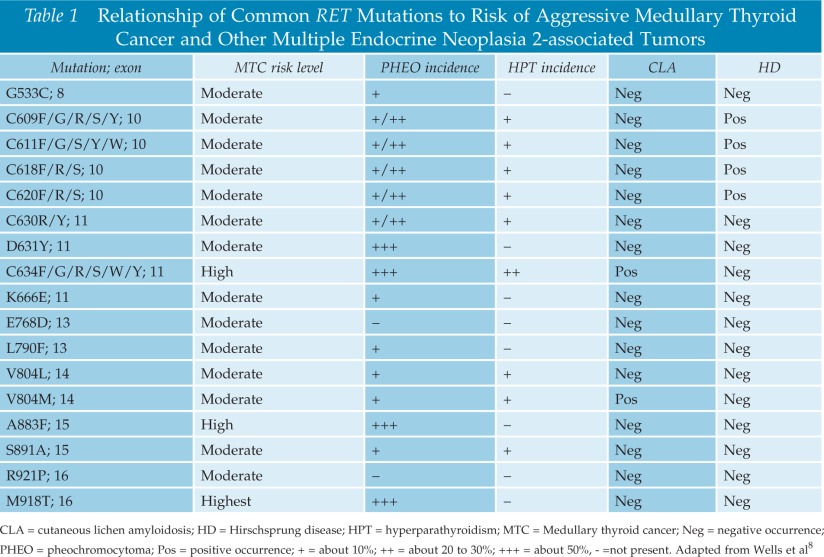
- More than 100 mutations, duplications, insertions, or deletions associated with hereditary MTC have been described and are:Associated with varying levels of tumor aggressiveness and genotype-phenotype correlations with other tumors such as pheochromocytomas, PHPT, and CLA
- The American Thyroid Association (ATA) classifies hereditary MTC into several risk categories:The highest risk (HST) category includes patients with: MEN2B and the RET codon M918T mutation
- The high risk (H) category includes patients with:RET codons C634 and A883F mutations
- All remaining mutations are grouped in the:Moderate risk (MOD) category
-

- What is Head and Neck Surgery?:
- It is a surgical sub-specialty that deals mainly with benign and malignant tumors of the head and neck region, including:
- The scalp, facial region, eyes, ears, nose, nasal fossae, paranasal sinuses, oral cavity, pharynx (nasopharynx, oropharynx, hypopharynx), larynx (supraglotic larynx, glottis larynx, subglotic larynx), thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, salivary glands (parotid glands, submandibular glands, sublingual glands, minor salivary glands), soft tissues of the neck, skin of the head and neck region.
- The head and neck surgeon’s work area:Does not cover tumors or diseases of the brain and other areas of the central nervous system or those of the cervical spine:This is the neurosurgeon field.
- The scalp, facial region, eyes, ears, nose, nasal fossae, paranasal sinuses, oral cavity, pharynx (nasopharynx, oropharynx, hypopharynx), larynx (supraglotic larynx, glottis larynx, subglotic larynx), thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, salivary glands (parotid glands, submandibular glands, sublingual glands, minor salivary glands), soft tissues of the neck, skin of the head and neck region.
- Among the diagnostic procedures performed by the head and neck surgeon, are the following:
- Nasopharyngolaryngoscopy:
- Performed to examine, evaluate and, possibly perform a biopsy, of oral cavity, pharyngeal and laryngeal lesions.
- Nasopharyngolaryngoscopy:
- The surgeries most commonly performed by the head and neck surgeon are:
- Total or near total thyroidectomies
- Hemithryoidectomies (lobectomies)
- Comprehensive neck dissections
- Selective neck dissections
- Maxillectomies:
- Total maxillectomy
- Subtotal maxillectomy
- Infrastructure maxillectomy
- Suprastructure maxillectomy
- Medial maxillectomy
- Mandibulectomy:
- Segmental
- Marginal
- Tracheostomy
- Salivary gland surgeries:
- Parotid gland operations:
- Limited superficial parotidectomy with identification and preservation of the facial nerve
- Superficial parotidectomy with identification and preservation of the facial nerve
- Near total parotidectomy with identification and preservation of the facial nerve
- Total parotidectomy
- Submandibular gland resection
- Sublingual gland resection
- Parotid gland operations:
- Resection of tumors of the oral cavity:
- Glossectomy
- Resection of the floor of the mouth tumors
- Resection of tumors of the pharynx
- Resection of tumors of the larynx
- Split-thickness skin grafts
- Full-thickness skin grafts
- Sentinel lymph node mapping and sentinel lymph node biopsy
- Resection of malignant skin tumors (BCC, SCC, melanoma) of the head and neck region
- It is a surgical sub-specialty that deals mainly with benign and malignant tumors of the head and neck region, including:
- The formation of the head and neck surgeon includes mastering the following subjects:
- Surgical Anatomy
- History and Basic Principles of Head and Neck Surgery
- Epidemiology, Etiology, and Pathology of Head and Neck Diseases
- Diagnostic Radiology of the Head and Neck Region
- Tumors of the Scalp, Skin and Melanoma
- Eyelids and Orbit
- Nasal Cavity and Paranasal Sinuses
- Skull Base and Temporal Bone
- Lips and Oral Cavity
- Pharynx and Esophagus
- Larynx and Trachea
- Cervical Lymph Nodes
- Thyroid and Parathyroid Glands
- Salivary Glands
- Neurogenic Tumors and Paragangliomas
- Soft Tissue Tumors
- Bone Tumors and Odontogenic Lesions
- Reconstructive Surgery
- Oncologic Dentistry and Maxillofacial Prosthetics
- Principles of Radiation Oncology
- Principles of Chemotherapy
- Molecular Oncology, Genomics and Immunology
- Nutrition
- Biostatistic
-
Rodrigo Arrangoiz MS, MD, FACS a head and neck surgeon / endocrine surgeon / surgical oncologist and is a member of Sociedad Quirúrgica S.C at the America British Cowdray Medical Center in Mexico City:

- Rodrigo Arrangoiz MS, MD, FACS:
- Is a member of the American Head and Neck Society

-
- He is a member of the American Thyroid Association:





