- The basis and need for elective nodal treatment in head and neck cancer:
- Have been based largely on surgical series evaluating pathologic nodal involvement found on elective neck dissection in patients with clinically negative necks
- In a consecutive series of 1,081 head and neck cancer patients undergoing radical neck dissection:
- The incidence of pathologic node involvement:
- Was 33% among those undergoing elective neck surgery
- The pathologic findings identified the nodal stations at risk by tumor site:
- To establish the rationale for selective neck dissection (SND) as the elective surgical procedure
- The incidence of pathologic node involvement:
- Several reports have summarized the risk for metastases and nodal stations at risk
- Some general observations from such data can be made:
- Regarding larynx cancers:
- Candela reported the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) experience in determining the patterns of cervical nodal metastases in 247 larynx cancer patients undergoing radical neck dissections:
- Seventy-eight underwent elective radical neck dissection whereas 118 underwent immediate radical dissection for clinically node-positive disease
- The majority of patients (n = 189) were supraglottic larynx and 58 were glottic
- Pathologic nodal involvement:
- Was found in 37% undergoing elective neck dissection
- It is noted that cervical nodes spread in a similar fashion whether the patients are clinically node negative or positive:
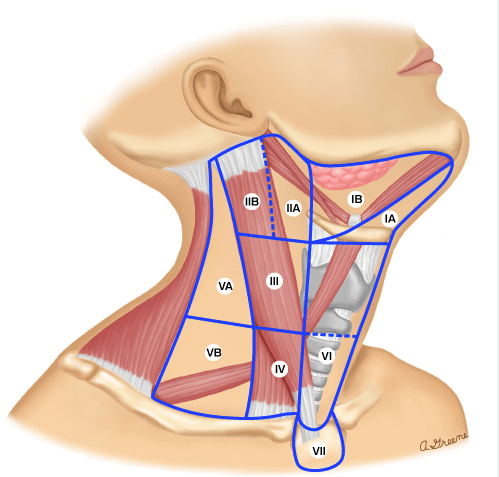
- With predominant involvement of:
- Level II and III jugular nodes
- With predominant involvement of:
- In clinically node-negative patients:
- The incidence of involvement of level I and V:
- Is less than 5% with less than 10% involvement of level IV
- The incidence of involvement of level I and V:
- In node-positive patients:
- The incidence of level IV node increases from 15% to 31% with greater involvement of levels II and III
- In clinically node-positive patients:
- Very rarely did patients present with isolated level I nodal metastases without involvement of the jugular nodes
- Candela reported the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) experience in determining the patterns of cervical nodal metastases in 247 larynx cancer patients undergoing radical neck dissections:
- Regarding larynx cancers:
- Shah and Candela reported that among oropharynx or hypopharynx cancers:
- Treated with elective radical neck dissection:
- Occult metastases are found in 26%
- Level I and V were involved in only 1.4%:
- Always in association with nodal disease at level II to IV
- No skip metastases were reported
- Among oropharynx patients:
- Levels II to IV were predominantly involved
- Among hypopharynx lesions:
- The primary levels involved were levels II and III
- In patients clinically node positive undergoing therapeutic neck dissection:
- The incidence of level I and V involvement increased to about 10% to 15%:
- However, levels II to IV were predominantly involved
- Level V involvement:
- Only occurred in association with nodal involvement at levels II to IV
- Whereas the incidence isolated level I involvement without levels II to IV involvement (“skip metastasis”):
- Occurred in 0.4%:
- Thus, based on these studies, elective treatment of the neck in oropharynx or hypopharynx can be directed at levels II to IV
- Occurred in 0.4%:
- The incidence of level I and V involvement increased to about 10% to 15%:
- Treated with elective radical neck dissection:
- Among oral cavity patients:
- The incidence of nodal disease was 34% on elective evaluation
- The majority of metastatic nodes involved:
- Levels I to III:
- With only 1.5% incidence of skip metastasis to level IV
- Levels I to III:
- Level V involvement:
- Is found in only 0.5% with occult disease simultaneously involving other levels
- Among those undergoing therapeutic neck dissections:
- The incidence of level IV involvement increased to 20%
- Level V was 4% always restricted to lower gum or floor of mouth primary sites
- The need for elective treatment not only relates to the estimated probability of nodal involvement and usually is implemented when the risk is 20% or greater but also relates to the morbidity of such treatment as well as the adequacy of coverage