- Prognostic role of estrogen receptor (ER) and HER2 in DCIS:
- In observational studies:
- ER status – 5 of 26 studies found a statistically significant lower risk of ipsilateral breast tumor recurrence (IBTR) in ER positive cases
- HER2 status – 10 out of 27 studies reported a significant increase in the risk of recurrences to be associated with HER2 expression
- Limitations of these observational studies were:
- Small sample size (events) in the majority of the studies
- Selection bias
- Treatment-related confounding:
- ER expression is inversely associated and HER2 expression is positively associated with:
- Adverse histologic features in DCIS
- Therefore, ER negative or HER2 amplification in DCIS:
- Is more likely to receive adjuvant treatment that ER positive or HER2 negative DCIS when ER or HER2 status is not known:
- Potentially masking the true association
- Is more likely to receive adjuvant treatment that ER positive or HER2 negative DCIS when ER or HER2 status is not known:
- The probability of masking of the true association:
- Increases greatly if the biomarker also has predictive characteristics
- ER expression is inversely associated and HER2 expression is positively associated with:
- In observational studies:
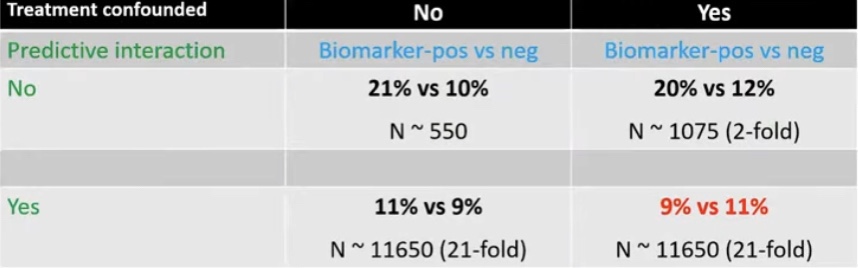
- How to eliminate treatment-related confounding:
- The study population should have random treatment allocation:
- Cohorts from randomized controlled trials
- Case-control studies matching by treatment:
- Does not permit investigation of predictive characteristics of the biomarker
- Multivariable / adjusted analysis:
- Power remains an issue
- The study population should have random treatment allocation:
- Biomarker cohort study:

- UK, Australia and New Zealand DCIS trial Cuzick J et al Lancet Oncol. 2011; Houghton J eta al Lancet 2003):
- 2X2 randomized trial comparing the effectiveness of radiotherapy and tamoxifen in reducing recurrences in patients with complete locally excised DCIS
- # of patients 1694
- The 2X2 factorial design permits investigation pertaining to both adjuvant treatments in DCIS
- After a median follow-up of 12.7 years, there have been 162 invasive and 197 DCIS events in these patients:
- 17 unknown
- Total 376
- In the study they observed that in patient with ER positive DCIS:
- They identified areas within the ducts that were ER negative in the same lesion
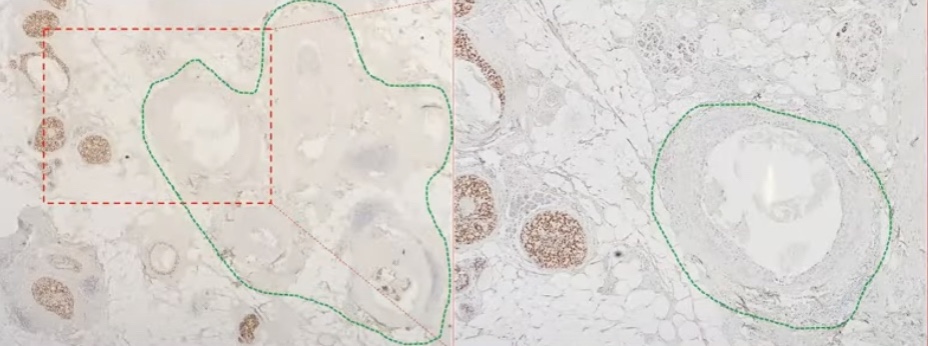

- In these study 11% of patients were identified to have multi-clonal DCIS:
- Clonal method:

- Estrogen receptor (ER) expression and recurrence:
- ER negative (multi-clonal) DCIS is associated with:
- A five fold increase of in situ ipsilateral breast event
- A three fold increase in overall ipsilateral breast event
- Invasive ipsilateral breast event is not statistically increased
- ER negative (multi-clonal) DCIS is associated with:

- The results show that the clonal method:
- Is superior to the standard method in predicting IBE and DCIS-IBE
- Progesterone receptor (PgR):
- Was not significantly associated with recurrence in ER positive DCIS
- It was not an independent predictor in multivariable models
- Inclusion of PGR did not significantly improve multivariable models
- HER2 expression and recurrence:
- HER2 positively was identified in 55% of the cases of DCIS:
- Compared to invasive breast cancer which is around 15% to 20%
- The expression of HER2 was associated with a two fold increase in IBE and in situ IBE
- HER2 positively was identified in 55% of the cases of DCIS:
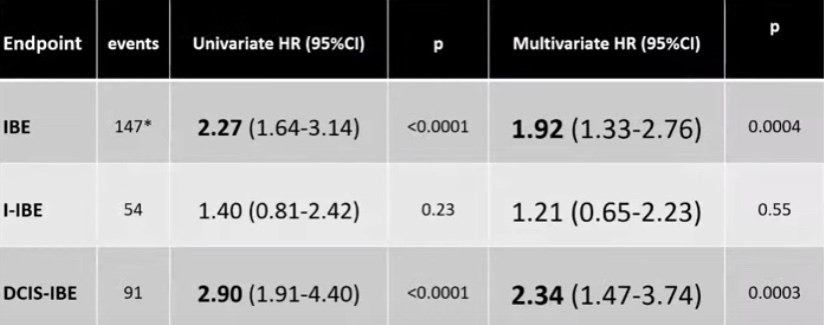
Univariable Analysis N = 713; Multivariable Analysis N = 612
IBE: Ipsilateral breast event, I-IBE: Invasive IBE, In situ IBE
- HER2 status (post-ERBB2-reflex test) and recurrence:
- HER2 status (ERBB2 reflexes) as a predictor of recurrence:
- Is associated with nearly a three fold increase in IBE and in situ IBE
- Is associated with an increase risk of I-IBE but it did not reach statistical significance
- HER2 status (ERBB2 reflexes) as a predictor of recurrence:

Comparison of HER2 positive (3+ of IHC 2+ and ERBB2 mRNA expression > 1.1007 vs. HER2 negative (0, 1+ or 2+ with ERBB2 mRNA expression </= 1.1007
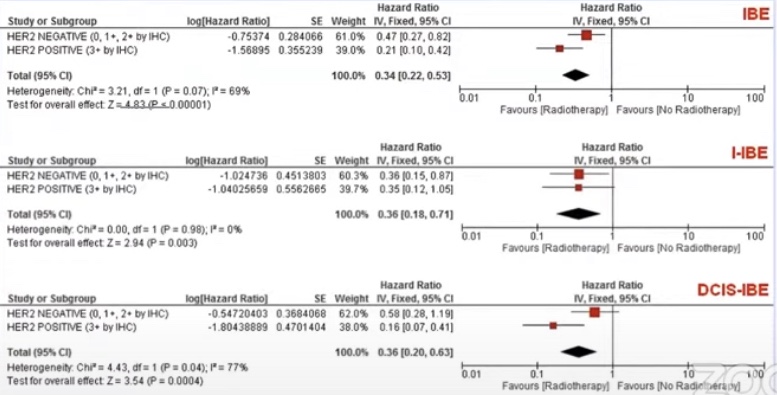
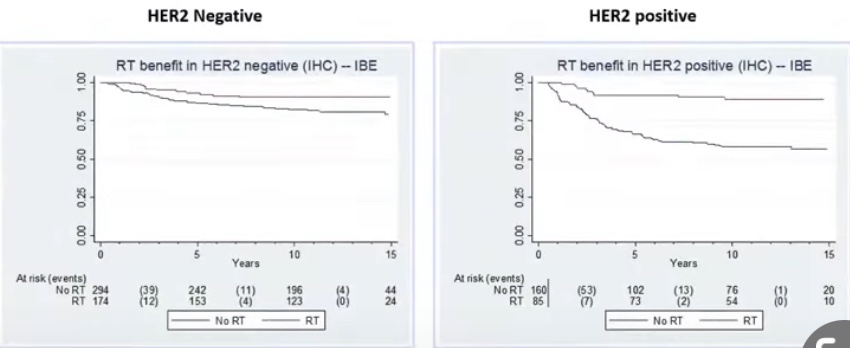
- Radiation therapy benefit:
- In HER2 positive disease was much larger as compared to HER 2 negative disease (statistically significant difference)
- In HER2 negative DCIS radiation therapy reduced events by 53% compared to 80% in HER2 positive disease
- In conclusion:
- ER is a strong prognostic factor:
- IBE mOR 3.33 for clinical method
- HER2 is a strong prognostic factor:
- IBE HR 2.84 for ERBB2-reflexes status
- Radiotherapy benefit greater in HER2 positive DCIS:
- HR 0.21 vs 0.47:
- En by greater benefit in reducing DCIS-IBE
- HR 0.21 vs 0.47:
- ER and HER2 evaluation should be routinely carried out?
- ER is a strong prognostic factor:

- Endocrine therapy considerations:
- NSABP-B24:
- ER is a predictor of tamoxifen benefit
- Ipsilateral ER status is not a predictor of contralateral breast cancer (CBC) risk or tamoxifen benefit in preventing CBC
- NSABP-B24:
- Combining the data from the RTOG 9804 trial and the UK/ANZ DCIS trial in the low risk DCIS (< 10 mm):
- Can we recommend radiation therapy only to ER – negative or HER2 – positive DCIS?
- The effect size and predictive benefit are an excellent fit to the RTOG 9804 results if 15% to 20% of patients in the trial were HER2 positive (proportion similar to the UK/ANZ DCIS trial)
- With that proportion of HER2 expression:
- 15 year cumulative IBE rates (15.1% overall) in the RT arm of the trial would be 9% in HER2 negative (0.6% per years, same as CBC risk) and 26% in HER2 positive disease
- Can we recommend radiation therapy only to ER – negative or HER2 – positive DCIS?

