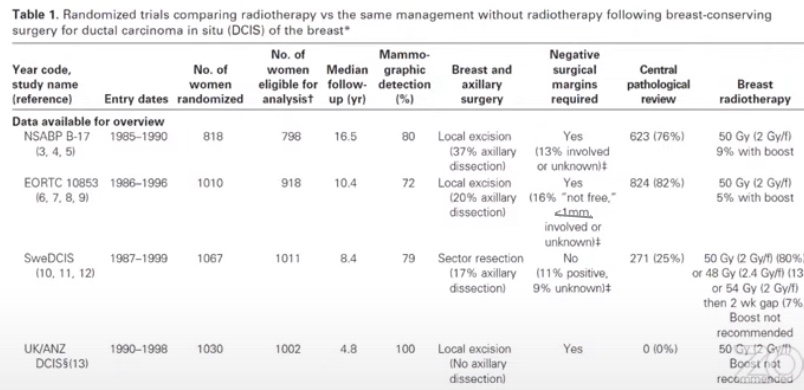
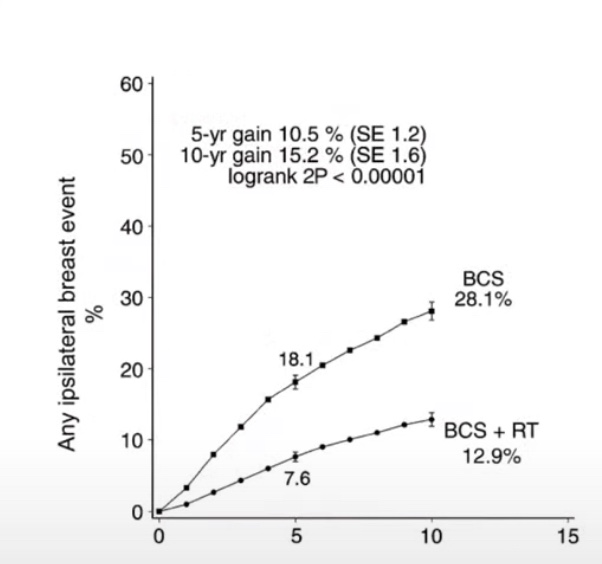
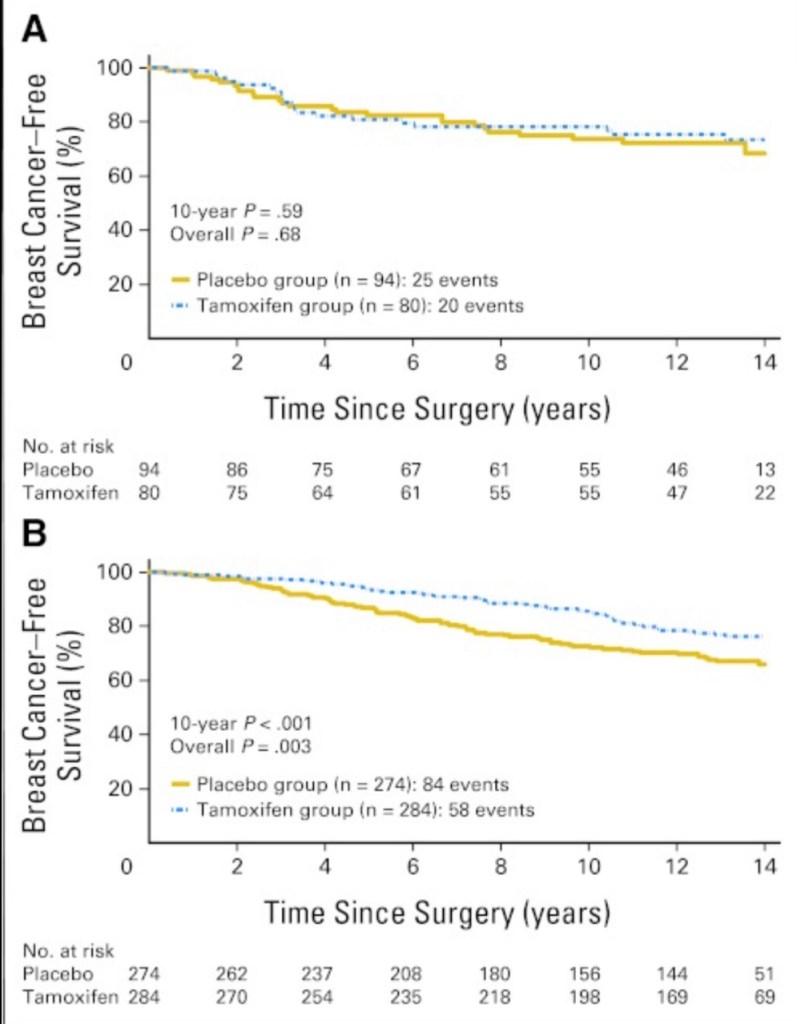
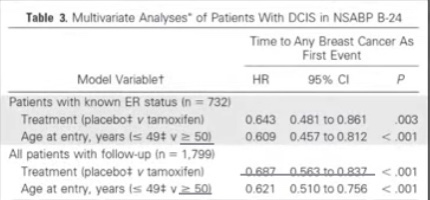
Published by Rodrigo Arrangoiz MS, MD, FACS, FSSO
My name is Rodrigo Arrangoiz I am a breast surgeon/ thyroid surgeon / parathyroid surgeon / head and neck surgeon / surgical oncologist that works at Center for Advanced Surgical Oncology in Miami, Florida.
I was trained as a surgeon at Michigan State University from (2005 to 2010) where I was a chief resident in 2010. My surgical oncology and head and neck training was performed at the Fox Chase Cancer Center in Philadelphia from 2010 to 2012. At the same time I underwent a masters in science (Clinical research for health professionals) at the University of Drexel. Through the International Federation of Head and Neck Societies / Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center I performed a two year head and neck surgery and oncology / endocrine fellowship that ended in 2016.
Mi nombre es Rodrigo Arrangoiz, soy cirujano oncólogo / cirujano de tumores de cabeza y cuello / cirujano endocrino que trabaja Center for Advanced Surgical Oncology en Miami, Florida.
Fui entrenado como cirujano en Michigan State University (2005 a 2010 ) donde fui jefe de residentes en 2010. Mi formación en oncología quirúrgica y e n tumores de cabeza y cuello se realizó en el Fox Chase Cancer Center en Filadelfia de 2010 a 2012. Al mismo tiempo, me sometí a una maestría en ciencias (investigación clínica para profesionales de la salud) en la Universidad de Drexel. A través de la Federación Internacional de Sociedades de Cabeza y Cuello / Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center realicé una sub especialidad en cirugía de cabeza y cuello / cirugia endocrina de dos años que terminó en 2016.
View all posts by Rodrigo Arrangoiz MS, MD, FACS, FSSO