- Myth:
- Fluid collections in the lactating breast require operative incision and drainage or aspiration alone
- Science:
- As surgeons have moved away from large incision and drainage procedures performed on the lactating breast in the operating room setting:
- They have turned to minimally invasive aspiration approach:
- However, aspiration alone can result in incomplete drainage
- They have turned to minimally invasive aspiration approach:
- Unlike simple breast cysts, abscesses and galactoceles in the lactating breast contain breastmilk:
- Which is highly viscous and loculated (Figure):
- Therefore, a needle aspiration alone will likely remove only part of the fluid collection, particularly if it is chronic
- If a needle aspiration is successful in removing the entire volume of an acute collection:
- The area can refill with milk very quickly and require repeated procedures
- Which is highly viscous and loculated (Figure):
- As surgeons have moved away from large incision and drainage procedures performed on the lactating breast in the operating room setting:
- Treatment:
- Lactational abscess and infected galactocele:
- Require drainage for source control
- Drainage may also be appropriate for symptomatic noninfected galactoceles:
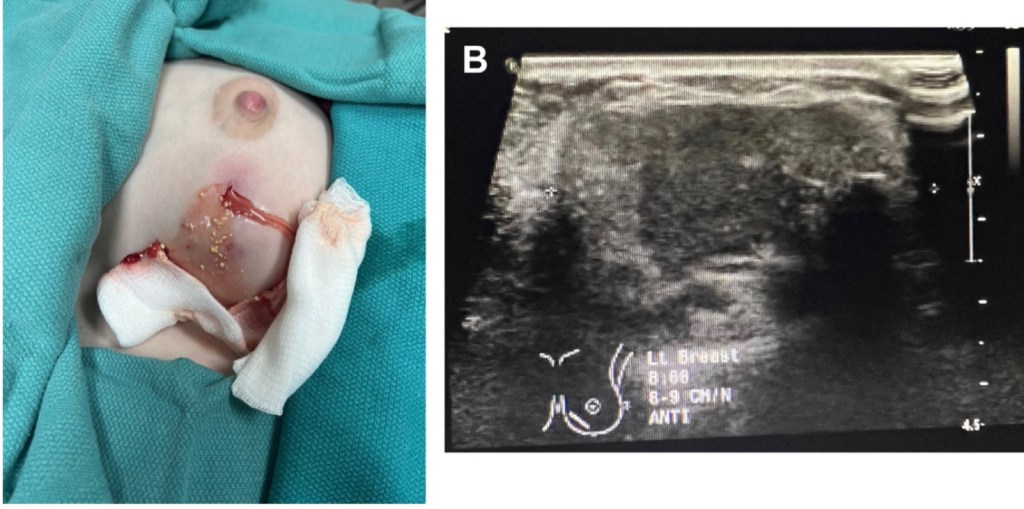
- Small stab incision and drain placement will definitively resolve fluid collections in the lactating breast:
- The small stab incision allows for access to the cavity with an instrument that can be used to disrupt loculations and provide complete drainage, such as a hemostat
- A stent or drain can be placed to allow passive decompression of the area for 3 to 5 days:
- This could involve a Penrose drain, Seromacath, Blake drain, or other wicks such as a small foley catheter:
- Drains should be placed to gravity rather than suction
- This could involve a Penrose drain, Seromacath, Blake drain, or other wicks such as a small foley catheter:
- Small stab incision and drain placement will definitively resolve fluid collections in the lactating breast:
- In addition to the surgical management, many patients developing fluid collections during lactation require treatment of idiopathic or iatrogenic hyperlactation:
- Patients should not be instructed to massage their breast:
- As this results in tissue necrosis and phlegmon development
- Ice and antiinflammatory medication by mouth should be recommended for symptomatic relief
- Antibiotics may be indicated if significant surrounding cellulitis exists
- Patients should not be instructed to massage their breast:
- Lactational abscess and infected galactocele:
#Arrangoiz #BreastSurgeon #CancerSurgeon #SurgicalOncologist #Surgeon #Surgeon #Doctor #MountSinaiMedicalCenter #MSMC #Miami #Mexico
