- The cytoskeleton provides the structural framework for the cell:
- It is composed of three main types of protein polymers:
- Actin filaments
- Intermediate filaments
- Microtubules
- Actin filaments:
- Are found in nearly all types of cells
- They form a cortical layer beneath the plasma membrane of most cells
- They form the stress fiber of fibroblasts
- They form the cytoskeleton of microvilli of intestinal epithelial cells.
- In muscle cells:
- The interaction between the heads of myosin (thick filaments) and actin (thin filaments):
- Requires hydrolysis of ATP to separate the filaments at the end of the power stroke
- Calcium and troponin C (an actin-associated protein):
- Are also required to expose the binding site for myosin on the actin filament
- The interaction between the heads of myosin (thick filaments) and actin (thin filaments):
- Intermediate filaments:
- Are a heterogeneous group of proteins
- That extend from the nucleus to the cell surface.
- They interact with other cytoskeletal filaments and binding proteins to produce their effects.
- Microtubules:
- Arise from the centrosome:
- With the cell’s microtubule-organizing center being located near the nucleus
- Microtubules are in a constant dynamic equilibrium:
- Between assembly and disassembly
- Movement of cellular components, such as vacuoles, along the microtubules requires:
- ATP and either of two associated proteins:
- Kinesin:
- For movement away from the centrosome
- Dynein:
- For movement toward it.
- Kinesin:
- ATP and either of two associated proteins:
- Cilia and flagella contain:
- Columns of doublet microtubules in a 9-2 arrangement:
- Nine doublets in a circle surrounding two central doublets
- Movement is accomplished when the doublets slide along each other:
- In a process mediated by dynein and fueled by hydrolysis of ATP.
- Columns of doublet microtubules in a 9-2 arrangement:
- Microtubules also play an important role in cell division:
- Assembly of the mitotic spindle involves:
- Replication and splitting of the microtubule-organizing center:
- Into the two spindle poles and reorganization of the cytoskeletal microtubules to form the:
- Spindle apparatus.
- Into the two spindle poles and reorganization of the cytoskeletal microtubules to form the:
- Replication and splitting of the microtubule-organizing center:
- Assembly of the mitotic spindle involves:
- Arise from the centrosome:
- It is composed of three main types of protein polymers:
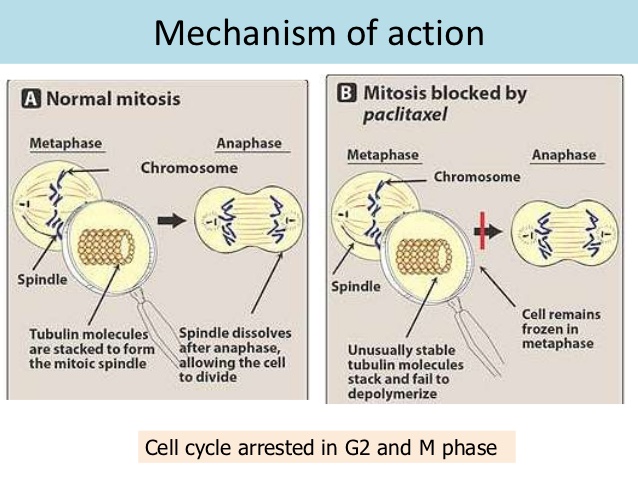
- Taxanes:
- Function as mitotic inhibitors:
- By inhibiting depolymerization of the mitotic spindle:
- Which results in a “frozen” mitosis.
- By inhibiting depolymerization of the mitotic spindle:
- Paclitaxel:
- Is a natural taxane that prevents depolymerization of cellular microtubules.
- Function as mitotic inhibitors:
- The vinca alkaloids (e.g., vinblastine, vincristine):
- Also inhibit cell division:
- But by disrupting the mitotic spindle.
- Also inhibit cell division:
- Doxorubicin (Adriamycin):
- Intercalates between DNA base pairs:
- Impairs the progression of topoisomerase II:
- Which unwinds DNA for transcription
- Impairs the progression of topoisomerase II:
- Intercalates between DNA base pairs:

#Arrangoiz
#CancerSurgeon
#Cancer
#Teacher
#SurgicalOncologist
#CirujanoOncologo
#HeadandNeckSurgeon
#CirujanodeCabezayCuello
#SociedadQuirurgica
#Oncologia
#Oncology
#BreastCancer
#BreastSurgeon
#CancerdeMama
#CirujanodeMama
