- Desmoplastic melanoma (DM) is a rare, fibrosing subtype of melanoma:
- It accounts for 1% to 4 % of all melanoma cases.
- It is seen typically in elderly patients:
- Mean age at diagnosis:
- 66 years
- Usually it is found in sun damaged patients:
- Frequently located on:
- The head and neck:
- 53% of the cases
- Extremities:
- 26% of the cases
- Trunk:
- 20% of the cases
- The head and neck:
- Frequently located on:
- Men are reportedly two times more susceptible to DM as compared to women.
- Mean age at diagnosis:
- Usually, DMs present as:
- Non-pigmented, skin colored and scar-like indurated dermal papules, plaques or nodules:
- Due to lack of prominent clinical features:
- The tumors are detected late and most reach significant depth (reticular dermis or even deeper) at the time of diagnosis.
- Due to lack of prominent clinical features:
- Non-pigmented, skin colored and scar-like indurated dermal papules, plaques or nodules:

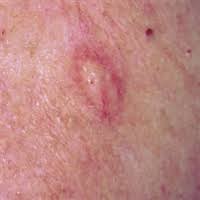
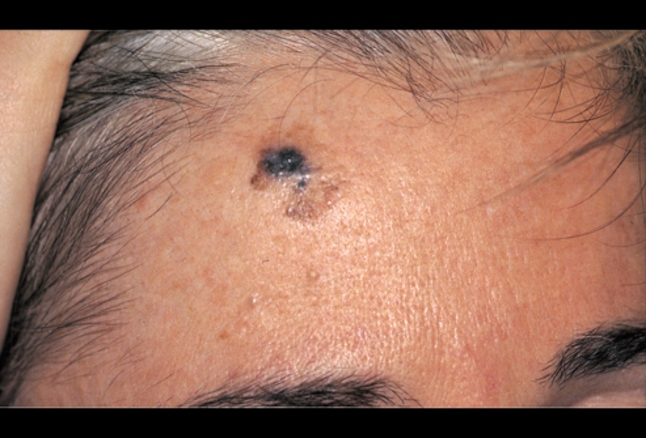
- The differential diagnosis includes:
- Neurofibroma
- Spindle cell sarcoma
- Schwannoma
- Dermatofibroma
- Blue nevus
- Fibromatosis
- Scar
- DMs are sometimes associated with neurotropism with a tendency of perineural invasion:
- In these cases the term ‘desmoplastic neurotrophic melanoma’ is used to describe the tumors.
- Dermoscopic evaluation demonstrates that:
- The majority of DMs lacked melanocytic pigmented structures.
- All cases of DM had at least one melanoma-specific structure, like:
- Atypical vascular structures
- Peppering
- Blue-white veil
- Atypical globules
- Crystalline structures
- Atypical network
- In some cases dense collagen fibrils
- Histologically:
- The lesions have dermal and subcutaneous spindle-shaped cells arranged as a single infiltrate or organized into fascicles.
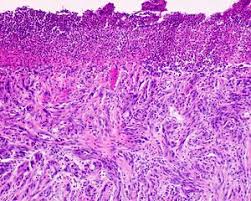
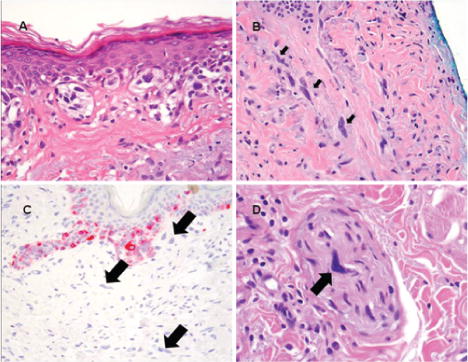
- DMs are subdivided into:
- Pure DM (pDM):
- Comprising of entirely or almost entirely desmoplastic components,
- Combined DM (cDM):
- Comprising of a desmoplastic component admixed with a non-desmoplastic component.
- Pure DM (pDM):
- Proteins are downstream of up regulated genes:
- Identification of specific proteins associated with melanoma progression may provide prognostic indicators and therapeutic targets.
- DM and superficial spreading melanoma (SSM) have variably expressed proteins:
- Desmoglein 1 is one protein expressed higher during the development of DM than SSM.
- Heat shock proteins (HSPs) are uniformly elevated in SSM in comparison with DM:
- HSPs have been postulated to:
- Protect tumor cells from destruction by innate immunity
- Promote cell-cycle dysregulation
- Promote invasion
- Promote neovascularization
- HSPs have been postulated to:
- Immunohistochemically:
- The tumor cells of DM often fail to react with many antibodies such as melan A:
- But are usually positive for:
- S100 protein
- Nerve growth factor receptor
- SOX10 gene.
- But are usually positive for:
- The tumor cells of DM often fail to react with many antibodies such as melan A:
- Neurofibromin 1 is the gene most commonly mutated in DM:
- 93% of the cases:
- Usually resulting in non-functional proteins.
- 93% of the cases:
- SOX10 protein is a transcription factor important for neural crest, peripheral nervous system, and melanocytic development:
- SOX10 is highly specific and sensitive for malignant melanoma:
- Including DM and spindle cell melanomas:
- Being expressed 98% of the time
- Including DM and spindle cell melanomas:
- SOX10 is highly specific and sensitive for malignant melanoma:
- Surgical excision is the current treatment of choice:
- Yet, there have not been established optimal margins:
- Because of the depth of invasion at the time of diagnosis, achieving clear surgical margins upon extirpation becomes difficult.
- This is especially true in large resections of aesthetically sensitive areas, such as the head and neck.
- Because of the depth of invasion at the time of diagnosis, achieving clear surgical margins upon extirpation becomes difficult.
- Low incidence of lymph node involvement:
- Ranging from 4% to 14%:
- This distinguishes it from other types of melanoma.
- Low incidence of regional lymph node metastases suggests that elective lymph node dissection is not indicated.
- Ranging from 4% to 14%:
- There may be benefit to identifying, and histologically evaluating, nerves encountered during the resection.
- In patients with positive surgical margins:
- One study showed a local recurrence rate of 14% in radiotherapy patients as compared with 54% in those who did not:
- Thus, evidence shows adjuvant radiotherapy should be the standard treatment of DM patients with:
- Positive margins
- Advanced Clark level
- Breslow thickness 4 mm or greater
- Recurrent DM
- Inoperable DM
- DM with neurotropism (DNM)
- Thus, evidence shows adjuvant radiotherapy should be the standard treatment of DM patients with:
- One study showed a local recurrence rate of 14% in radiotherapy patients as compared with 54% in those who did not:
- Yet, there have not been established optimal margins:
- The type of DM was found to be associated with disease recurrence and patient survival:
- Positive sentinel node biopsy was more frequently found in cDMs as compared to pDMs
- cDM patients have a worse prognosis as compared to pDM patients
Rodrigo Arrangoiz MS, MD, FACS a head and neck / surgical oncologist and is a member of Sociedad Quirúrgica S.C at the America British Cowdray Medical Center in Mexico City:
-
He is an expert in the management of skin cancer including MELANOMA.
-
If you have any questions about the management of melanoma please fill free to contact Dr. Arrangoiz.
-
Article on Melanoma published by Dr. Arrangoiz:
-





