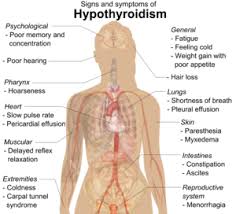
Hypothyroidism results from insufficient production and secretion of thyroid hormones.
-
This is most commonly due to disturbance within the thyroid gland itself, (primary hypothyroidism) or within the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid axis (secondary hypothyroidism).
Causes of primary hypothyroidism
1. Associated with goitre
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis)
- Iodine deficiency
- Inherited defects of biosynthesis
- Drug induced (amiodarone, lithium, phenylbutazone)
- Maternal transmission (e.g. anti-thyroid drugs)
2. Not associated with goitre
- Atrophic thyroiditis
- Iatrogenic (e.g. radioiodine, surgery, neck irradiation)
- Congenital anomaly (e.g. thyroid agenesis)
3. Self-limiting
- Transient thyroiditis
- Post partum thyroiditis
- Iatrogenic (overtreatment with anti-thyroid medication)

The prevalence of hypothyroidism is estimated at around 2% of adult women and 0.2% of men, rising to 5% to 10% in women over 65