A. The maxillary artery supplies the deep structures of the face.
1. It branches from the external carotid artery just deep to the neck of the mandible.
B. Structure:
1. The maxillary artery, the larger of the two terminal branches of the external carotid artery:
– Arises behind the neck of the mandible, and is at first imbedded in the substance of the parotid gland.
2. It passes forward between the ramus of the mandible and the sphenomandibular ligament, and then runs, either superficial or deep to the lateral pterygoid muscle, to the pterygopalatine fossa.
3. It supplies the deep structures of the face.
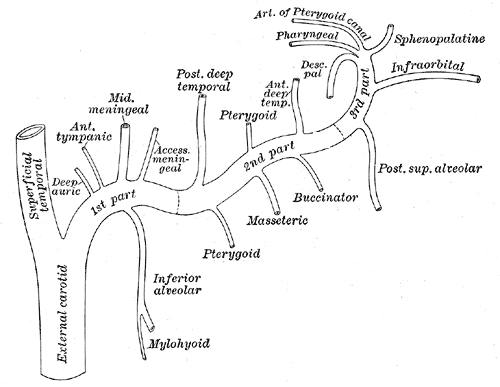
4. May be divided into:
– Mandibular portion (first part / bone portion)
– Pterygoid portion (second part / muscular portion)
– Pterygopalatine portions (third part).
C. First portion:
1. The first or mandibular portion (or bony portion) passes horizontally forward, between the neck of the mandible and the sphenomandibular ligament:
– Where it lies parallel to and a little below the auriculotemporal nerve.
2. It crosses the inferior alveolar nerve, and runs along the lower border of the lateral pterygoid muscle.
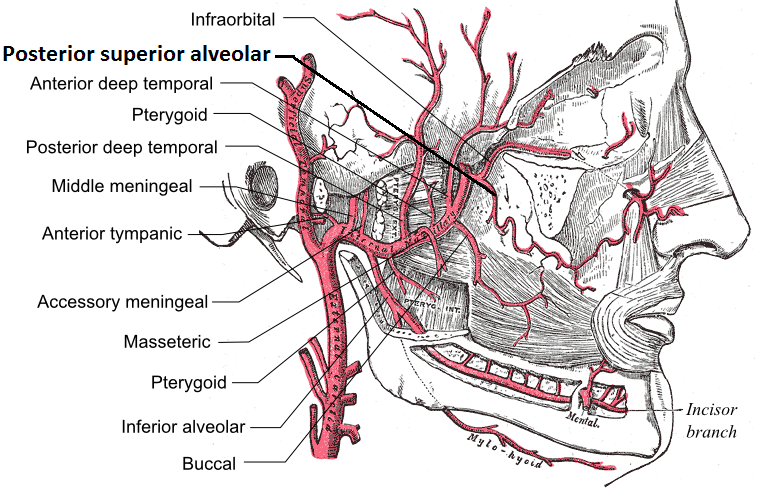
3. Branches include:
– Deep auricular artery
– Anterior tympanic artery
– Middle meningeal artery
– Inferior alveolar artery: which gives off its mylohyoid branch just prior to entering the mandibular foramen
– Accessory meningeal artery
D. Second Portion:
1. The second or pterygoid portion (or muscular portion) runs obliquely forward and upward under cover of the ramus of the mandible and insertion of the temporalis muscle:
– On the superficial (very infrequently on the deep) surface of the lateral pterygoid muscle.
– It then passes between the two heads of origin of this muscle and enters the pterygopalatine fossa.
2. Branches include:
– Masseteric artery
– Pterygoid branches
– Deep temporal arteries
= Anterior and posterior
– Buccal (buccinator) artery
E. Third Portion:
1. The third or pterygopalatine portion lies in the pterygopalatine fossa in relation with the pterygopalatine ganglion.
2. This is considered the terminal branch of the maxillary artery.
3. Branches include:
– Sphenopalatine artery: also known as the nasopalatine artery which is the terminal branch of the maxillary artery
– Descending palatine artery:
= Greater palatine artery
= Lesser palatine artery
– Infraorbital artery
– Posterior superior alveolar artery
– Artery of pterygoid canal
-Pharyngeal artery
– Middle superior alveolar artery (could be a branch of the infraorbital artery)
– Anterior superior alveolar arteries (could be a branch of the infraorbital artery)
Cirugía General y Gastrointestinal
Michigan State University
Cirugía Oncológica
Drexel University
Certificado por el Colegio Americano de Cirugía
Sociedad Quirúrgica S.C.
Hospital ABC Santa Fé
Av. Carlos Graef Fernández #154
Col. Tlaxala, Delg. Cuajimalpa
México, D.F. 05300
Tel: 1103 – 1600 Ext 4515 a la 4517
Fax:1664 – 7164
